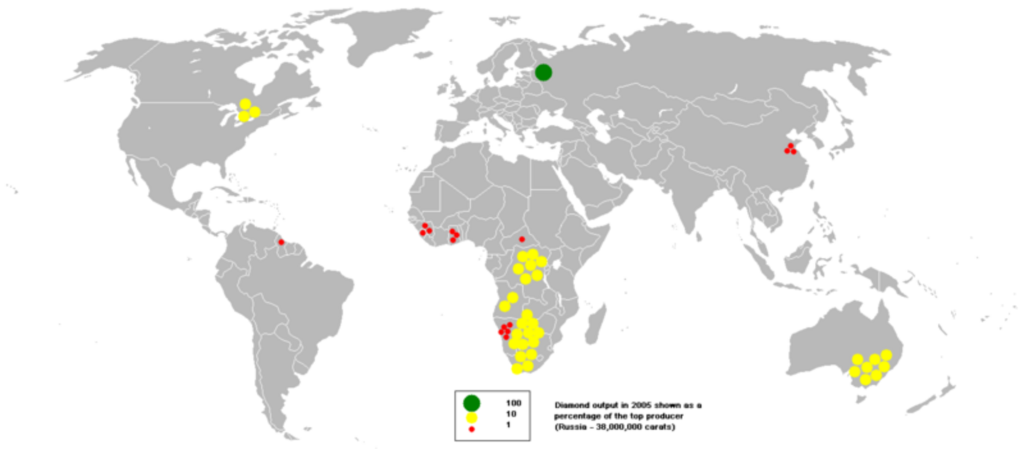
Diamond producing countries in Africa remain at the center of the global diamond industry, as the continent supplies some of the highest quality rough diamonds and accounts for a large percentage of worldwide output. Africa is not only home to the richest diamond mines but also hosts both large-scale corporate mining and extensive artisanal operations. With countries such as Botswana, South Africa, and Angola leading in production, Africa continues to influence global trade and diamond markets. Let’s dive into Top 10 Diamond Producing Countries in Africa and their output.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Meaning of Diamond Production
- Importance of Africa in the Global Diamond Industry
- Top 10 Diamond Producing Countries in Africa
- Comparison Table of Top 10 Producers in Africa
- Other Diamond-Producing Countries in Africa
- Characteristics of African Diamond Mining
- Challenges of Diamond Production in Africa
- Future Outlook of African Diamond Industry
- Conclusion
Meaning of Diamond Production
Diamond production refers to the extraction of rough diamonds from natural deposits, usually measured in carats. One carat equals 0.2 grams, and production levels in Africa are often expressed in millions of carats annually. Production includes both gem-quality diamonds, which are used in jewelry, and industrial-quality stones, which are applied in drilling, cutting, and grinding industries.
Importance of Africa in the Global Diamond Industry
Africa has historically been the world’s leading supplier of diamonds, and the continent remains dominant today. While countries outside Africa such as Russia and Canada are large producers, the African continent contributes more than half of global gem-quality stones. Mines such as Jwaneng in Botswana, Venetia in South Africa, and Catoca in Angola are among the most productive worldwide.
Top 10 Diamond Producing Countries in Africa
1. Botswana
Botswana is Africa’s leading diamond producer, with annual output of about 25.1 million carats. The country is home to the Jwaneng and Orapa mines, operated by Debswana, a partnership between De Beers and the government of Botswana. Diamonds account for a significant portion of Botswana’s GDP and have transformed it into one of the most stable economies in Africa.
2. Democratic Republic of Congo
The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) produces between 8.3 and 9.9 million carats annually, making it the second-largest African producer. Most of its diamonds are industrial grade, sourced largely from the Kasai region. Despite vast reserves, challenges such as artisanal mining dominance and regulatory difficulties affect the sector.
3. Angola
Angola produces around 9.8 million carats annually, ranking third in Africa. The Catoca mine, operated in partnership with Russian firms, is one of the world’s largest kimberlite mines. Angola’s government is working to increase transparency and attract investment to boost diamond revenues.
4. South Africa
South Africa produces about 5.9 million carats annually. Historically famous for mines such as Kimberley and Cullinan, the country remains a significant producer. Venetia mine, operated by De Beers, is currently the largest source of diamonds in South Africa.
5. Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe contributes approximately 4.5 million carats each year, with most production centered in the Marange diamond fields. While controversial due to past governance and human rights issues, Zimbabwe’s output remains one of the highest in Africa.
6. Namibia
Namibia produces 2.1–2.3 million carats annually, with a unique focus on marine mining. De Beers Marine Namibia extracts diamonds from the Atlantic seabed, making the country’s industry one of the most technologically advanced in Africa.
7. Sierra Leone
Sierra Leone produces around 600,000–700,000 carats annually. Known historically for “blood diamonds,” the country has made significant progress in reforming its industry. Major mining areas include Koidu and Tongo.
8. Lesotho
Lesotho contributes about 0.7 million carats annually (≈700,000 carats), but its global significance comes from the high quality and large size of stones mined at Letseng. Diamonds from Lesotho often fetch premium prices on the international market.
9. Ghana
Ghana produces between 300,000 and 400,000 carats annually. While small in volume compared to major producers, Ghana’s diamonds are primarily gem-quality and mined through both industrial and artisanal operations.
10. Tanzania
Tanzania produces around 200,000–300,000 carats annually, mostly from the Williamson diamond mine. While production is modest, the country is known for steady contributions to Africa’s diamond exports.
Comparison Table of Top 10 Producers in Africa
| Rank | Country | Annual Production (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Botswana | ~25.1 million carats |
| 2 | DRC | ~8.3–9.9 million carats |
| 3 | Angola | ~9.8 million carats |
| 4 | South Africa | ~5.9 million carats |
| 5 | Zimbabwe | ~4.5 million carats |
| 6 | Namibia | ~2.1–2.3 million carats |
| 7 | Sierra Leone | ~600,000–700,000 carats |
| 8 | Lesotho | ~700,000 carats |
| 9 | Ghana | ~300,000–400,000 carats |
| 10 | Tanzania | ~200,000–300,000 carats |
Other Diamond-Producing Countries in Africa
| Country | Annual Production (Approx.) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Central African Republic | ~300,000–400,000 carats | Mostly artisanal mining |
| Guinea | ~500,000–600,000 carats | Medium-to-lower grade stones |
| Liberia | ~150,000–200,000 carats | Small-scale production |
| Cameroon | ~100,000 carats | Emerging diamond sector |
Characteristics of African Diamond Mining
- Concentration of Production – A few countries such as Botswana, Angola, and DRC dominate Africa’s diamond output.
- Mix of Mining Scales – Africa combines large-scale corporate mines with widespread artisanal mining.
- Gem vs. Industrial Diamonds – Nations like Botswana focus on gem-quality stones, while DRC supplies mostly industrial-grade.
- Technological Diversity – From traditional artisanal methods to advanced marine mining in Namibia, Africa displays a range of techniques.
Challenges of Diamond Production in Africa
- Artisanal Mining Issues – Informal miners often lack regulation, leading to smuggling and lost revenue.
- Conflict Legacy – Countries like Sierra Leone and Liberia faced challenges with conflict diamonds.
- Governance and Transparency – Weak institutions and corruption sometimes undermine diamond revenues.
- Environmental Impact – Mining often causes land degradation, water pollution, and deforestation.
Future Outlook of African Diamond Industry
Africa’s diamond production is expected to remain strong due to large reserves and ongoing exploration. Investments in technology, transparency programs like the Kimberley Process, and responsible mining practices are improving the industry’s image. Countries such as Botswana and Namibia are also moving toward local beneficiation, where more diamonds are cut and polished domestically, adding economic value.
Frequently Asked Questions On Top 10 Diamond Producing Countries
1. Which country is the largest producer of diamonds in Africa?
Botswana is the largest diamond producer in Africa, with an annual output of about 25.1 million carats.
2. Which African countries produce the highest quality diamonds?
Lesotho, Botswana, and South Africa are known for producing some of the highest quality and largest gem-quality diamonds.
3. How many African countries produce diamonds?
More than 15 African countries produce diamonds, but the top 10 dominate overall production.
4. What is the difference between gem-quality and industrial diamonds in Africa?
Gem-quality diamonds are used in jewelry and are highly valuable, while industrial diamonds are used in drilling, cutting, and grinding industries.
5. Which African countries produce diamonds offshore?
Namibia is unique for its offshore marine diamond mining in the Atlantic Ocean.
6. Why are diamonds important to Africa’s economy?
Diamonds generate billions of dollars in export earnings, create jobs, and contribute significantly to national GDP in countries such as Botswana and Angola.
7. What challenges face diamond production in Africa?
Challenges include artisanal mining issues, smuggling, corruption, environmental damage, and the historical problem of conflict diamonds.
8. Which African country produces fewer diamonds but of very high value?
Lesotho produces around 700,000 carats annually, but its stones are often larger and fetch higher market prices.
9. Are all diamonds from Africa considered conflict diamonds?
No, most African diamonds today are mined under regulations like the Kimberley Process, which prevents conflict diamonds from entering legal markets.
10. Will Africa remain the leading producer of diamonds in the future?
Yes, due to its vast reserves, Africa is expected to remain central to global diamond production for decades, with Botswana, Angola, and the DRC leading.
SEE ALSO: TOP 10 Copper Producing Countries in Africa and Their Output
Conclusion – Top 10 Diamond Producing Countries
Africa continues to be the world’s backbone in diamond production, with the top 10 diamond producing countries in Africa accounting for the majority of gem-quality diamonds on global markets. Botswana, DRC, Angola, and South Africa lead the list, while smaller producers such as Lesotho and Sierra Leone contribute unique high-quality stones. Despite challenges such as artisanal mining and governance issues, the continent’s diamond industry holds great promise, both in economic development and in maintaining its central role in global supply.
