WAEC/NECO/JAMB Physics Past Questions and Answers

2025 Physics PRACTICAL, Theory and objectives.
Scroll down for NECO 2025 PHYSICS practical QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. OBJECTIVES AND THEORY
Scroll down for NECO 2025 PHYSICS practical QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. OBJECTIVES AND THEORY
scroll down
scroll down
Physics is a crucial subject in both the WAEC, NECO and JAMB examinations, and understanding its core concepts can significantly improve your chances of excelling in these exams. One of the most effective ways to prepare for the Physics exams is by practicing with past questions. Past questions give insight into the type of questions that frequently appear and help you develop strategies for answering them. In this hall, we will highlight some key past questions and answers for Physics, covering various topics typically in the WAEC, NECO, GCE and JAMB exams.
Read Also
PHYSICS PAST QUESTIONS and ANSWERS SECTION 1. (1–100) OBJS
1. The SI unit of force is
A. joule
B. newton
C. watt
D. kilogram
Answer: B
2. What is the acceleration due to gravity on Earth?
A. 9.8 m/s²
B. 10.5 m/s²
C. 8.5 m/s²
D. 9.2 m/s²
Answer: A
3. Which of the following is not a vector quantity?
A. Velocity
B. Acceleration
C. Displacement
D. Speed
Answer: D
4. A body in motion continues in a straight line unless acted upon by an external force. This is
A. Newton’s first law
B. Newton’s second law
C. Newton’s third law
D. Archimedes’ principle
Answer: A
5. Power is defined as
A. work per unit force
B. force × distance
C. work per unit time
D. energy per unit mass
Answer: C
6. Which instrument is used to measure electric current?
A. Voltmeter
B. Ammeter
C. Galvanometer
D. Thermometer
Answer: B
7. Which of these is a scalar quantity?
A. Force
B. Momentum
C. Pressure
D. Weight
Answer: C
8. The unit of pressure is
A. pascal
B. watt
C. newton
D. joule
Answer: A
9. The turning effect of a force is known as
A. acceleration
B. torque
C. pressure
D. impulse
Answer: B
10. The upward force that a fluid exerts on an object is called
A. tension
B. drag
C. buoyant force
D. friction
Answer: C
11. A machine has a velocity ratio of 5 and an efficiency of 80%. Its mechanical advantage is
A. 4.0
B. 5.0
C. 6.0
D. 0.8
Answer: A
12. A substance that can flow and take the shape of its container is a
A. liquid only
B. solid
C. fluid
D. gas only
Answer: C
13. Which of these is a non-renewable energy source?
A. Solar
B. Wind
C. Coal
D. Hydro
Answer: C
14. The instrument used to measure temperature is the
A. thermometer
B. voltmeter
C. micrometer
D. ammeter
Answer: A
15. Which of the following is not a property of light?
A. Reflection
B. Refraction
C. Conduction
D. Dispersion
Answer: C
16. A concave mirror forms a real, inverted image when the object is
A. at the focus
B. beyond the center of curvature
C. between the pole and focus
D. at the pole
Answer: B
17. What type of lens is used to correct short-sightedness?
A. Convex lens
B. Cylindrical lens
C. Concave lens
D. Plano-convex lens
Answer: C
18. The speed of light in vacuum is approximately
A. 3.0 × 10⁸ m/s
B. 3.0 × 10⁶ m/s
C. 1.5 × 10⁸ m/s
D. 2.5 × 10⁷ m/s
Answer: A
19. A body is in equilibrium if
A. the resultant force is zero
B. it is moving in a circle
C. it is accelerating
D. force acts in one direction
Answer: A
20. One horsepower is equal to
A. 746 watts
B. 1000 watts
C. 600 watts
D. 500 watts
Answer: A
21. A hydrometer is used to measure
A. temperature
B. pressure
C. density
D. relative density
Answer: D
22. The process by which heat is transferred in solids is called
A. convection
B. radiation
C. conduction
D. evaporation
Answer: C
23. Which of the following is a vector quantity?
A. Work
B. Energy
C. Time
D. Acceleration
Answer: D
24. A transformer operates on the principle of
A. direct current
B. electrostatics
C. mutual induction
D. magnetic repulsion
Answer: C
25. In projectile motion, the horizontal component of velocity is
A. increasing
B. constant
C. decreasing
D. zero
Answer: B
26. Which of these instruments is used to measure relative humidity?
A. Thermometer
B. Barometer
C. Hygrometer
D. Anemometer
Answer: C
27. Which electromagnetic wave has the highest frequency?
A. Microwave
B. Radio wave
C. Gamma ray
D. Infrared
Answer: C
28. The angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray is
A. twice the angle of incidence
B. equal to angle of incidence
C. 90°
D. sum of angle of incidence and angle of reflection
Answer: A
29. Latent heat is
A. heat required to raise temperature
B. heat required to change state
C. heat lost during radiation
D. heat used in conduction
Answer: B
30. Which material is a good conductor of electricity?
A. Plastic
B. Rubber
C. Copper
D. Wood
Answer: C
31. Which of these can be attracted by a magnet?
A. Aluminium
B. Copper
C. Plastic
D. Iron
Answer: D
32. The moment of a force depends on
A. mass and area
B. distance and time
C. force and distance
D. mass and speed
Answer: C
33. A nuclear reaction that produces energy in the sun is
A. fission
B. fusion
C. ionization
D. conduction
Answer: B
34. Ohm’s law states that
A. V = I/R
B. V = I × R
C. V = R/I
D. V = R + I
Answer: B
35. A wave in which particles move perpendicular to the direction of wave is
A. longitudinal
B. transverse
C. mechanical
D. electromagnetic
Answer: B
36. The area under a velocity-time graph gives
A. speed
B. distance
C. force
D. acceleration
Answer: B
37. An echo is heard when sound is reflected from a surface at least
A. 1 m away
B. 17 m away
C. 34 m away
D. 50 m away
Answer: B
38. Which of the following is not an effect of electric current?
A. Magnetic effect
B. Chemical effect
C. Light effect
D. Sound effect
Answer: D
39. An object floats in a liquid when its
A. weight is greater than upthrust
B. weight is less than upthrust
C. weight equals upthrust
D. density is higher than liquid
Answer: C
40. The slope of a distance-time graph represents
A. acceleration
B. speed
C. momentum
D. displacement
Answer: B
41. Radio waves are used in
A. cooking
B. medical imaging
C. broadcasting
D. sterilizing equipment
Answer: C
42. Which of these has the least resistance?
A. Silver
B. Wood
C. Glass
D. Rubber
Answer: A
43. A convex lens can be used as
A. rear-view mirror
B. diverging lens
C. magnifying glass
D. flashlight reflector
Answer: C
44. What is the frequency of a wave with a period of 0.01 seconds?
A. 0.01 Hz
B. 10 Hz
C. 100 Hz
D. 0.1 Hz
Answer: C
45. The quantity of matter in a body is its
A. weight
B. volume
C. mass
D. density
Answer: C
46. The center of mass of a uniform meter rule lies at
A. 0 cm
B. 25 cm
C. 50 cm
D. 75 cm
Answer: C
47. A wave whose vibration is in the same direction as motion is
A. longitudinal
B. transverse
C. circular
D. stationary
Answer: A
48. Which of these is a renewable energy source?
A. Natural gas
B. Coal
C. Wind
D. Diesel
Answer: C
49. The pressure in a liquid increases with
A. temperature
B. depth
C. surface area
D. height of the container
Answer: B
50. The efficiency of a machine is defined as
A. MA ÷ VR × 100
B. MA × VR × 100
C. VR ÷ MA × 100
D. MA + VR × 100
Answer: A
Physics Past Questions and Answers for WAEC, NECO, GCE/JAMB
51. The boiling point of water increases with
A. decrease in pressure
B. increase in pressure
C. constant temperature
D. increase in volume
Answer: B
52. A current of 2 A flows through a resistor of 3 Ω. What is the potential difference across it?
A. 6 V
B. 5 V
C. 1.5 V
D. 0.67 V
Answer: A
53. A neutral atom becomes a negative ion when it
A. loses a proton
B. gains an electron
C. gains a neutron
D. loses an electron
Answer: B
54. In which medium does sound travel fastest?
A. Air
B. Water
C. Vacuum
D. Metal
Answer: D
55. A fuse is used in an electric circuit to
A. increase the voltage
B. reduce resistance
C. break the circuit when excessive current flows
D. store current
Answer: C
56. The mass of a body is 10 kg. What is its weight on Earth?
A. 10 N
B. 100 N
C. 9.8 N
D. 98 N
Answer: D
57. A freely falling object falls with
A. constant speed
B. constant velocity
C. uniform acceleration
D. decreasing acceleration
Answer: C
58. Which of the following statements is correct?
A. Heat flows from cold to hot
B. Heat flows from hot to cold
C. Heat does not flow
D. Heat flow depends on volume
Answer: B
59. The property of a body to resist a change in its state of motion is
A. energy
B. momentum
C. inertia
D. mass
Answer: C
60. An object thrown vertically upward returns to the ground due to
A. air resistance
B. acceleration
C. gravity
D. inertia
Answer: C
61. The image formed by a plane mirror is
A. real and inverted
B. virtual and upright
C. real and diminished
D. enlarged and real
Answer: B
62. Radioactivity was discovered by
A. Einstein
B. Newton
C. Becquerel
D. Rutherford
Answer: C
63. Which law states that pressure applied on a fluid is transmitted equally in all directions?
A. Boyle’s Law
B. Pascal’s Principle
C. Archimedes’ Principle
D. Charles’ Law
Answer: B
64. The rise of a liquid in a capillary tube is due to
A. viscosity
B. cohesion
C. surface tension
D. gravity
Answer: C
65. An object of mass 20 kg moving with velocity 10 m/s has kinetic energy of
A. 2000 J
B. 1000 J
C. 100 J
D. 4000 J
Answer: B
66. A transformer with more turns in the secondary coil than the primary coil is a
A. step-down transformer
B. step-up transformer
C. induction coil
D. primary transformer
Answer: B
67. Which of the following is not a unit of energy?
A. Joule
B. Calorie
C. Newton
D. Kilowatt-hour
Answer: C
68. The heat capacity of a body is
A. the heat required to raise the temperature of unit mass
B. the heat required to raise the temperature of the body by 1°C
C. the amount of heat absorbed in boiling
D. the amount of heat lost during radiation
Answer: B
69. The period of a simple pendulum depends on
A. its mass
B. its length
C. its amplitude
D. gravity and mass
Answer: B
70. When two objects move toward each other, the relative velocity is
A. the sum of their individual velocities
B. the difference of their velocities
C. the product of their velocities
D. zero
Answer: A
71. An electric bell works on the principle of
A. electrostatics
B. magnetism
C. electromagnetic induction
D. electromagnetism
Answer: D
72. The efficiency of a perfect machine is
A. 0%
B. 50%
C. 75%
D. 100%
Answer: D
73. A rocket works on the principle of
A. Newton’s first law
B. Newton’s second law
C. Newton’s third law
D. Law of inertia
Answer: C
74. The echo of a sound is heard after 0.2 seconds. What is the distance of the reflecting surface? (Speed of sound = 340 m/s)
A. 68 m
B. 34 m
C. 170 m
D. 340 m
Answer: A
75. X-rays are produced when
A. electrons move in a circuit
B. electrons strike a metal target at high speed
C. radioactive decay occurs
D. current flows through gas
Answer: B
76. The device used to convert mechanical energy to electrical energy is
A. transformer
B. battery
C. dynamo
D. diode
Answer: C
77. The loudness of a sound depends on its
A. frequency
B. amplitude
C. pitch
D. speed
Answer: B
78. Which of the following is not a characteristic of a wave?
A. Wavelength
B. Frequency
C. Velocity
D. Volume
Answer: D
79. The function of a commutator in a DC motor is to
A. increase current
B. reverse current direction
C. reduce resistance
D. convert AC to DC
Answer: B
80. Total internal reflection occurs when light
A. moves from air to glass
B. moves from glass to air at angle less than critical
C. moves from glass to air at angle greater than critical
D. moves along normal
Answer: C
81. The force that keeps an object in circular motion is
A. centrifugal force
B. frictional force
C. centripetal force
D. gravitational force
Answer: C
82. The rate of change of momentum is equal to
A. mass × acceleration
B. force
C. impulse
D. velocity
Answer: B
83. Two resistors of 4 Ω and 6 Ω are connected in series. The total resistance is
A. 10 Ω
B. 2.4 Ω
C. 1.5 Ω
D. 24 Ω
Answer: A
84. The minimum distance between an object and its real image in a concave mirror is
A. radius of curvature
B. focal length
C. twice the focal length
D. infinity
Answer: C
85. A wire of length 2 m carries a current of 5 A in a magnetic field of 0.1 T perpendicular to it. What is the force on the wire?
A. 0.5 N
B. 1.0 N
C. 2.0 N
D. 10.0 N
Answer: B
86. The phenomenon that explains why the sky appears blue is
A. reflection
B. refraction
C. scattering
D. interference
Answer: C
87. Which of these is a unit of power?
A. Newton
B. Joule
C. Watt
D. Volt
Answer: C
88. If a body is acted upon by a net force, it will
A. remain at rest
B. move at uniform speed
C. accelerate
D. experience no motion
Answer: C
89. The main difference between a heat engine and an electric motor is
A. working substance
B. motion
C. energy conversion
D. speed
Answer: C
90. The nucleus of an atom is made up of
A. electrons and protons
B. protons and neutrons
C. electrons only
D. neutrons only
Answer: B
91. Which of the following does not involve the use of a lens?
A. Camera
B. Human eye
C. Periscope
D. Microscope
Answer: C
92. The energy stored in a stretched spring is
A. potential energy
B. kinetic energy
C. chemical energy
D. mechanical energy
Answer: A
93. A capacitor is used to
A. store charge
B. supply power
C. reduce current
D. increase voltage
Answer: A
94. The pressure at the bottom of a liquid is
A. the same as at the top
B. higher than at the top
C. lower than at the top
D. not measurable
Answer: B
95. Brownian motion provides evidence for
A. gravity
B. kinetic theory
C. Newton’s laws
D. thermodynamics
Answer: B
96. The temperature at which a substance changes from solid to liquid is
A. boiling point
B. latent heat
C. melting point
D. condensation point
Answer: C
97. A satellite stays in orbit due to
A. inertia
B. centripetal force
C. gravitational attraction
D. all of the above
Answer: D
98. A diode allows current to flow in
A. no direction
B. one direction
C. two directions
D. alternate direction
Answer: B
99. Which device converts sound energy to electrical energy?
A. Loudspeaker
B. Microphone
C. Amplifier
D. Earphone
Answer: B
100. Which of these is used to detect radiation?
A. Ammeter
B. Electroscope
C. Geiger-Müller tube
D. Barometer
Answer: C
100 Physics WAEC, NECO, GCE/JAMB past questions and answers to help with exam preparation:
1. What is the SI unit of force?
Answer: The SI unit of force is Newton (N).
2. A car accelerates from 5 m/s to 25 m/s in 10 seconds. What is the acceleration?
Answer:
Using the formula a = v − u/t, where:
- v = 25 (final velocity)
- u = 5 (initial velocity)
- t = 10
a=25−5/10=20/10=2 m/s²
3. What is the formula for kinetic energy?
Answer: The formula for kinetic energy is:
KE=1/2mv²
Where m is mass and v is velocity.
4. What is the principle of conservation of momentum?
Answer: The principle of conservation of momentum states that the total momentum of a closed system remains constant, provided no external forces act on it.
5. What happens to the pressure of a gas if the volume is reduced at constant temperature?
Answer: According to Boyle’s Law, if the volume of a gas is reduced at constant temperature, its pressure increases.
6. What is the formula for the speed of a wave?
Answer: The speed of a wave is given by the formula:
v = f×λ
Where f is frequency and λ is wavelength.
7. What is the unit of electric charge?
Answer: The unit of electric charge is Coulomb (C).
8. How is the frequency of a wave related to its period?
Answer: The frequency (f) of a wave is the reciprocal of its period (T),
f = 1/T
9. A current of 3 A flows through a resistance of 5 Ω. What is the potential difference across the resistance?
Answer: Using Ohm’s Law, V = I/R
Where I=3I = 3 A and R = 5R = 5 Ω,
V = 3 × 5 =15
100 Physics WAEC/JAMB past questions and answers continue…
10. Define work done in terms of force and displacement.
Answer: The work done is given by the formula:
W = F × d
Where FF is the force applied and dd is the displacement.
11. What is the relationship between the refractive index and the speed of light in a medium?
Answer: The refractive index n of a medium is the ratio of the speed of light in vacuum cc to the speed of light in the medium v,
n = c
12. What is the law of reflection?
Answer: The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
13. What is the formula for calculating the period of a simple pendulum?
Answer: The period (T) of a simple pendulum is given by:
T=2πLgT = 2
Where L is the length of the pendulum and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
14. If a wave has a frequency of 60 Hz and a wavelength of 5 meters, what is its velocity?
Answer: Using the wave velocity formula,
v=f×λ
Where f = 60f = 60 Hz and λ=5
v=60×5=300 m/s
15. What is Ohm’s Law?
Answer: Ohm’s Law states that the current (I) through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference (V) across it and inversely proportional to the resistance (R),
V=I/R
16. What happens to the gravitational force between two objects if the distance between them is doubled?
Answer: According to Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation, the gravitational force decreases by a factor of 4 when the distance between two objects is doubled.
17. What is the unit of power?
Answer: The unit of power is Watt (W), which is equivalent to one joule per second.
18. What is the frequency of a wave with a period of 0.2 seconds?
Answer: The frequency is the reciprocal of the period,
f = 1T=10.2=5 Hz
19. What is the relationship between current and resistance in a circuit at constant voltage?
Answer: According to Ohm’s Law, current is inversely proportional to resistance at constant voltage,
I=V/R.
Batch No, 2 100 Physics WAEC/JAMB past questions and answers
20. What is the unit of electric power?
Answer: The unit of electric power is the Watt (W), where
P = IVP = IV
Where P is power, I is current, and V is voltage.
21. What is the SI unit of energy?
Answer: The SI unit of energy is the Joule (J).
22. A body is dropped from a height. What is its initial velocity?
Answer: The initial velocity of a body dropped from a height is 0 m/s, since it starts from rest.
23. What is the difference between scalar and vector quantities?
Answer:
- Scalar quantities have only magnitude (e.g., mass, temperature, time).
- Vector quantities have both magnitude and direction (e.g., force, velocity, displacement).
24. What is the relationship between the force of attraction and the mass of two objects?
Answer: According to Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation, the force of attraction between two objects is directly proportional to the product of their masses,
F∝m1, m2, r2
Where m1 and m2 are the masses of the objects, and r is the distance between their centers.
25. What is the formula for calculating the electric field strength?
Answer: The electric field strength (E) is given by:
E = F/q
Where F is the force experienced by a test charge q.
26. What is the Doppler effect?
Answer: The Doppler effect is the change in frequency or wavelength of a wave as observed by someone who is moving relative to the source of the wave.
27. What is the law of conservation of energy?
Answer: The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only converted from one form to another.
28. What is the function of a capacitor in an electric circuit?
Answer: A capacitor stores electrical energy and releases it when needed. It can smooth out fluctuations in voltage and store energy for later use.
29. What is the formula for the gravitational potential energy of an object?
Answer: The formula for gravitational potential energy (PE) is:
PE = mgh
Where:
- m is the mass of the object
- g is the acceleration due to gravity
- h is the height above the ground.
30. How does the frequency of a wave relate to the pitch of sound?
Answer: The frequency of a sound wave determines its pitch. Higher frequency waves produce higher-pitched sounds, while lower frequency waves produce lower-pitched sounds.
31. What is the difference between longitudinal and transverse waves?
Answer:
- Longitudinal waves have particles vibrating in the same direction as the wave (e.g., sound waves).
- Transverse waves have particles vibrating perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation (e.g., light waves).
32. What is the principle behind the operation of a transformer?
Answer: A transformer operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a change in the magnetic flux in the primary coil induces an electromotive force (EMF) in the secondary coil.
33. What is the formula for the period of oscillation of a mass-spring system?
Answer: The period (T) of a mass-spring system is given by:
T = 2πmk
Where m is the mass attached to the spring and k is the spring constant.
34. What is the unit of frequency?
Answer: The unit of frequency is the Hertz (Hz), which represents one cycle per second.
35. What is meant by the term “electromagnetic spectrum”?
Answer: The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of all types of electromagnetic radiation, classified by wavelength or frequency, including radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.
36. How does the resistance of a conductor change with temperature?
Answer: For most materials, the resistance increases with an increase in temperature. This is because higher temperatures cause more frequent collisions of electrons with atoms, which increases resistance.
37. What is the function of a fuse in an electrical circuit?
Answer: A fuse protects an electrical circuit by breaking the circuit if the current exceeds a certain level, preventing damage to electrical components.
38. What is meant by the term “specific heat capacity”?
Answer: Specific heat capacity is the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a substance by 1°C.
39. What is the difference between heat and temperature?
Answer:
- Heat is the energy transferred between substances due to a temperature difference.
- Temperature is the measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance.
Batch no 3 WAEC/JAMB Physics Past Questions and Answers
40. How is the speed of sound affected by the medium through which it travels?
Answer: The speed of sound depends on the medium’s density and elasticity. Sound travels faster in solids than in liquids, and faster in liquids than in gases.
41. What is the unit of electric potential difference?
Answer: The unit of electric potential difference is the Volt (V).
42. What is the relationship between the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction in a plane mirror?
Answer: In a plane mirror, the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection.
θi = θr
Where θi is the angle of incidence and θr is the angle of reflection.
43. Define the term “magnetic field.”
Answer: A magnetic field is the region around a magnet or a current-carrying conductor where magnetic forces can be detected.
44. What is the principle of operation of an electric motor?
Answer: An electric motor operates on the principle that when a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a force. This force causes the conductor to move, producing rotational motion.
45. What is the frequency of a wave if its wavelength is 0.5 m and the wave speed is 10 m/s?
Answer: Using the wave equation v=f×λ
Where:
- v=10 m/s (speed of the wave)
- λ=0.5 m (wavelength)
Solving for frequency,
f=vλ=100.5=20
46. What is the formula for calculating the work done by a force?
Answer: The work done by a force is given by:
W=F×d×cos(θ)
Where F is the force, d is the displacement, and θ is the angle between the force and the direction of displacement.
47. What is the function of a diode in an electrical circuit?
Answer: A diode allows current to flow in one direction only, acting as a one-way valve for electrical current, thus preventing reverse current flow.
48. What is the electric field around a positively charged object?
Answer: The electric field around a positively charged object radiates outward from the object, meaning the field lines point away from the positive charge.
49. A gas is compressed at constant temperature. What happens to its volume and pressure?
Answer: According to Boyle’s Law, when the volume of a gas is decreased at constant temperature, the pressure increases.
50. Define “specific latent heat of fusion.”
Answer: Specific latent heat of fusion is the amount of heat required to change the state of 1 kg of a solid into a liquid without a change in temperature.
100 Physics WAEC/JAMB past questions and answers continued
51. What is the unit of resistance?
Answer: The unit of resistance is the Ohm (Ω).
52. What is the formula for calculating the refractive index?
Answer: The refractive index n is given by the formula:
n=sin(θi)sin(θr)
Where θi is the angle of incidence and θr is the angle of refraction.
53. What is the principle behind the operation of a hydroelectric power station?
Answer: A hydroelectric power station operates on the principle of converting the potential energy of water stored at a height into kinetic energy, which is then used to turn a turbine and generate electricity.
54. What is the relationship between the wavelength of light and its color?
Answer: Different colors of light have different wavelengths. Violet light has the shortest wavelength, while red light has the longest wavelength.
55. What is the formula for calculating the force of attraction between two point masses?
Answer: The formula for the gravitational force between two point masses is:
F=Gm1m2r2
Where:
- F is the gravitational force
- G is the gravitational constant
- m1 and m2 are the masses
- r is the distance between the masses.
56. What is meant by “elastic potential energy”?
Answer: Elastic potential energy is the energy stored in an elastic object (such as a stretched spring) when it is deformed (compressed or stretched).
57. What is the unit of electric charge?
Answer: The unit of electric charge is the Coulomb (C).
58. A body moves with constant speed. What is the work done by the force acting on it?
Answer: If a body is moving with constant speed, the work done by the force acting on it is zero, because the displacement and force are perpendicular, so the angle between them is 90° and cos(90∘)=0
59. What is the effect of an increase in temperature on the resistance of a conductor?
Answer: The resistance of a conductor generally increases with an increase in temperature, because the atoms of the conductor vibrate more at higher temperatures, impeding the flow of electrons.
Batch No 4, 100 Physics WAEC/JAMB past questions and answers
60. What is the role of the cathode in a cathode ray tube (CRT)?
Answer: In a cathode ray tube, the cathode is the negative electrode that emits electrons when heated. These electrons travel towards the positively charged anode, creating an electron beam that is used to form images on the screen.
61. What is the SI unit of power?
Answer: The SI unit of power is the Watt (W). It is defined as the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred, equal to one joule per second.
62. A current of 2 A flows through a resistor of 10 Ω. What is the power dissipated in the resistor?
Answer: Using the formula P=I2R where:
- I=2 A
- R=10 Ω
P=22×10=4×10=40 W
63. What is the principle of a hydraulic press?
Answer: The principle of a hydraulic press is based on Pascal’s Law, which states that pressure applied to a confined fluid is transmitted equally in all directions.
64. What is the relationship between current and potential difference in a conductor at constant temperature?
Answer: According to Ohm’s Law, current is directly proportional to the potential difference across a conductor at constant temperature.
I=V/R
65. What is the formula for calculating the energy of a photon?
Answer: The energy of a photon is given by the formula:
E=h×f
Where h is Planck’s constant and f is the frequency of the photon.
66. What is the unit of magnetic flux?
Answer: The unit of magnetic flux is the Weber (Wb).
67. What is meant by the term “terminal velocity”?
Answer: Terminal velocity is the constant velocity reached by an object falling through a fluid when the force of gravity is balanced by the resistive force of the fluid, resulting in zero net force and zero acceleration.
68. What is the difference between series and parallel circuits?
Answer:
- Series circuit: Components are connected end to end, so the current is the same through all components, but the total resistance is the sum of the individual resistances.
- Parallel circuit: Components are connected across common points, so the voltage across each component is the same, but the total resistance is less than the smallest individual resistance.
69. How does the speed of sound change with temperature?
Answer: The speed of sound increases with an increase in temperature because the molecules of the medium move faster, which allows sound waves to travel more quickly.
70. What is the formula for calculating the frequency of oscillation of a simple pendulum?
Answer: The frequency (f) of a simple pendulum is the reciprocal of the period (T), and is given by:
f=1T=12πgL
Where g is the acceleration due to gravity and L is the length of the pendulum.
71. What is the difference between an elastic and an inelastic collision?
Answer:
- Elastic collision: A collision in which both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved.
- Inelastic collision: A collision in which momentum is conserved, but kinetic energy is not conserved (some of the energy is transformed into other forms such as heat or sound).
72. What is the relationship between voltage and resistance in a series circuit?
Answer: In a series circuit, the total voltage is the sum of the individual voltages across each resistor, and the total resistance is the sum of individual resistances.
V/total = V1+V2
73. What is the use of a galvanometer in an electrical circuit?
Answer: A galvanometer is used to detect and measure small electrical currents. It can be modified to function as an ammeter or voltmeter by adding suitable resistors.
74. What is the relationship between frequency and wavelength of a sound wave?
Answer: The frequency and wavelength of a sound wave are inversely related. As the frequency increases, the wavelength decreases, and vice versa. This relationship is given by the equation:
v=f×λ
Where v is the speed of sound, ff is the frequency, and λ is the wavelength.
75. What is the formula for calculating the resistance of a wire?
Answer: The resistance RR of a wire is given by:
R=ρLA
Where:
- ρ\rho is the resistivity of the material
- L is the length of the wire
- A is the cross-sectional area of the wire.
76. What is the significance of the refractive index of a material?
Answer: The refractive index of a material determines how much light is bent, or refracted, as it passes through the material. A higher refractive index indicates that light travels more slowly in the material and is refracted more.
77. What is the formula for the kinetic energy of an object in motion?
Answer: The kinetic energy (KE) of an object in motion is given by:
KE=12mv²
Where m is the mass of the object and v is its velocity.
78. What happens when a magnetic field is applied to a conductor carrying current?
Answer: When a magnetic field is applied to a conductor carrying current, a force is exerted on the conductor, causing it to move. This is the principle behind the operation of electric motors.
79. What is the difference between a conductor and an insulator?
Answer:
- Conductor: A material that allows the flow of electric current, such as metals.
- Insulator: A material that does not allow the flow of electric current, such as rubber or plastic.
Batch No 5, 100 Physics past questions and answers
80. What is the function of an electromagnet?
Answer: An electromagnet is a magnet created by passing electric current through a coil of wire, usually wound around a ferromagnetic core. The strength of the magnetic field can be controlled by adjusting the current.
Batch no 5 WAEC/JAMB Physics Past Questions and Answers
81. What is the unit of magnetic field strength?
Answer: The unit of magnetic field strength is the Tesla (T).
82. What is the principle of operation of a transformer?
Answer: A transformer operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where a changing magnetic field in the primary coil induces an electromotive force (EMF) in the secondary coil, which can either step up or step down the voltage.
83. What is the formula for calculating gravitational potential energy?
Answer: The formula for gravitational potential energy is:
PE = mgh
Where:
- m is the mass of the object
- g is the acceleration due to gravity
- h is the height above the ground.
84. What is the relationship between current and voltage in a parallel circuit?
Answer: In a parallel circuit, the total current is the sum of the currents through each parallel branch, but the voltage across each branch is the same.
85. What is the difference between conductors and semiconductors?
Answer:
- Conductors are materials that allow electric current to flow easily (e.g., metals).
- Semiconductors have electrical conductivity between that of conductors and insulators (e.g., silicon), and their conductivity can be controlled by adding impurities (doping).
READ ALSO – Semiconductors and Diodes, Transistor and Logic Gates
86. What is the function of a fuse in an electrical circuit?
Answer: A fuse is a safety device that protects electrical circuits from excessive current by breaking the circuit when the current exceeds a safe level.
87. What is the law of reflection?
Answer: The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, and both are measured from the normal to the surface.
88. What is the SI unit of electric charge?
Answer: The SI unit of electric charge is the Coulomb (C).
89. How does the speed of light change when it passes from air into water?
Answer: The speed of light decreases when it passes from air into water because water is denser than air, and light slows down as it enters a denser medium.
100 Physics WAEC/JAMB past questions and answers continued
90. What is the relationship between the power of an electric appliance and its energy consumption?
Answer: The energy consumed by an electric appliance is directly proportional to its power and the time for which it is used. The formula is:
E = P × t
Where E is the energy consumed (in Joules), P is the power (in Watts), and t is the time (in seconds).
91. What is a dielectric material?
Answer: A dielectric material is an insulating material that can be polarized by an electric field, which increases the capacitance of a capacitor when placed between its plates.
92. What is the principle behind the operation of an electric motor?
Answer: An electric motor works on the principle that when a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a force, which causes the conductor to move. This motion is converted into rotational motion.
93. What is the formula for calculating the force of friction?
Answer: The force of friction (Ff) is given by:
Ff=μN
Where:
- μ is the coefficient of friction
- N is the normal force.
94. What is the difference between a convex lens and a concave lens?
Answer:
- Convex lens: A lens that converges light rays to a focal point (real image).
- Concave lens: A lens that diverges light rays, producing a virtual image.
95. What is the role of a capacitor in an electric circuit?
Answer: A capacitor stores electrical energy in the form of an electric field and can release this energy when needed. It is used in circuits to smooth voltage fluctuations and store energy.
96. What is the formula for the period of a simple harmonic oscillator?
Answer: The period T of a simple harmonic oscillator is given by:
T=2πmk
Where:
- m is the mass of the object
- k is the spring constant.
97. What is the difference between heat and temperature?
Answer:
- Heat is the transfer of energy due to a temperature difference.
- Temperature is the measure of the average kinetic energy of particles in a substance.
98. What is the difference between electric potential and electric potential energy?
Answer:
- Electric potential is the potential energy per unit charge at a specific point in an electric field.
- Electric potential energy is the energy stored in a charge due to its position in an electric field.
99. What happens when light passes through a prism?
Answer: When light passes through a prism, it bends (refracts) at different angles for different wavelengths. This results in the dispersion of light into its component colors, forming a spectrum.
100. What is the difference between a longitudinal wave and a transverse wave?
Answer:
- Longitudinal wave: In a longitudinal wave, the particles of the medium move parallel to the direction of wave propagation (e.g., sound waves).
- Transverse wave: In a transverse wave, the particles of the medium move perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation (e.g., light waves).
READ ALSO – Environmental Physics: Understanding Energy and Climate Change
These 100 WAEC, NECO/JAMB Physics Past questions and answers will further expand your understanding of Physics concepts and ensure that you are well-prepared for both WAEC, NECO and JAMB exams. Regular revision and practice with these problems will help you achieve success in your Physics exam.
2025 NECO PHYSICS PRACTICAL QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS





Physics specimens

2025 PHYSICS PRACTICAL ANSWERS
no 1bi

(2bi)
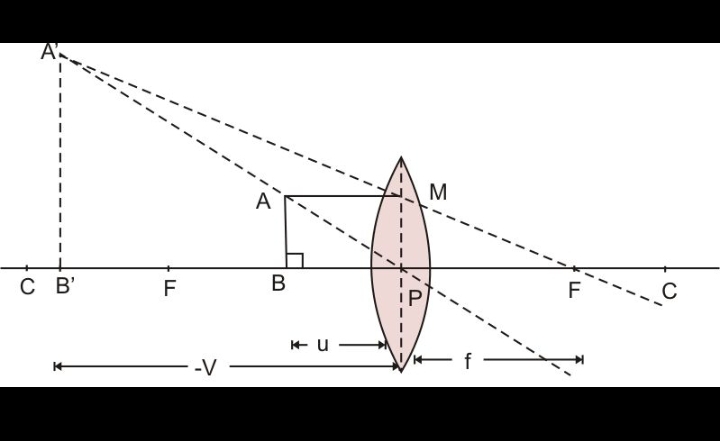
(2bii)

question 1. Answer

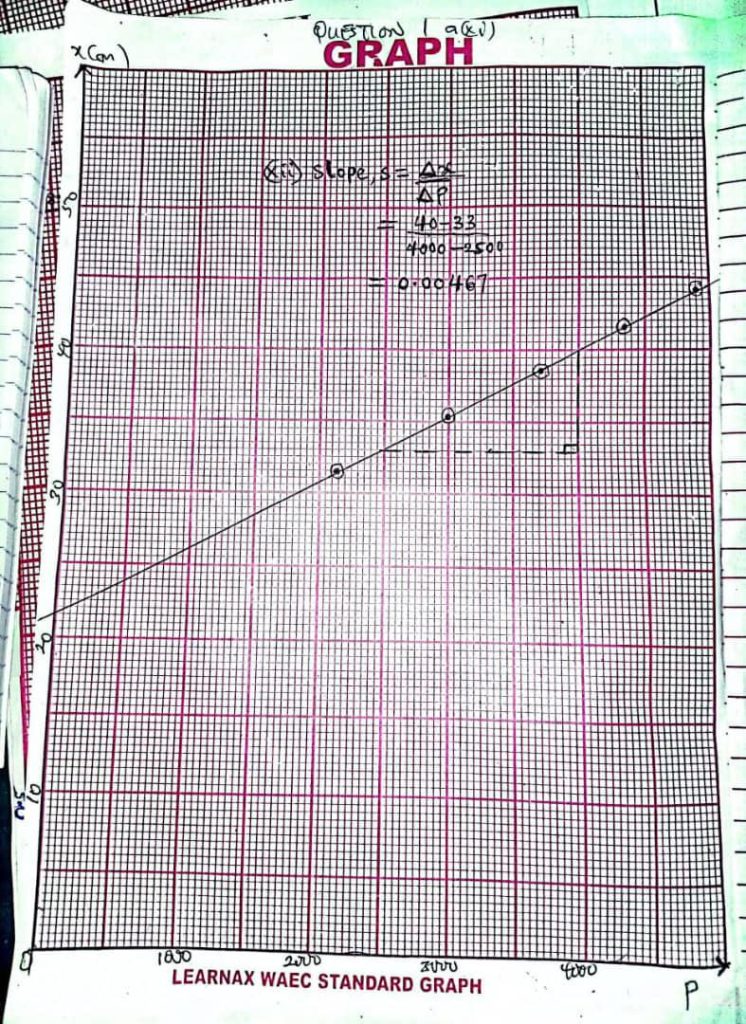
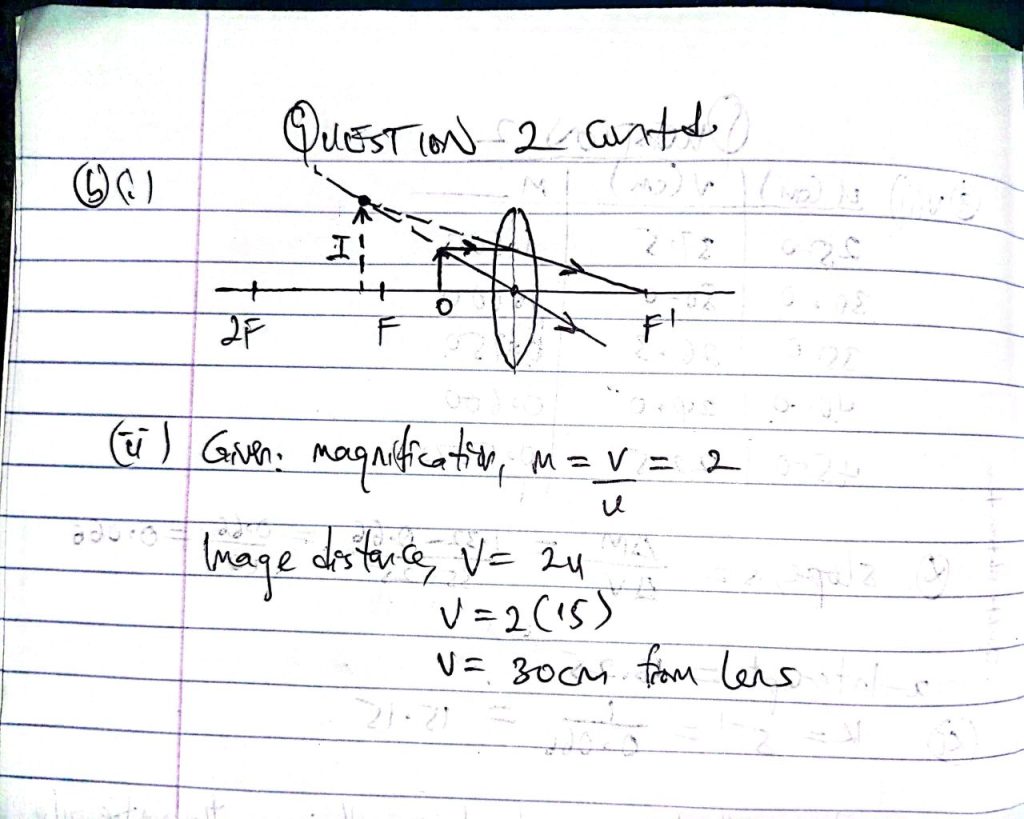


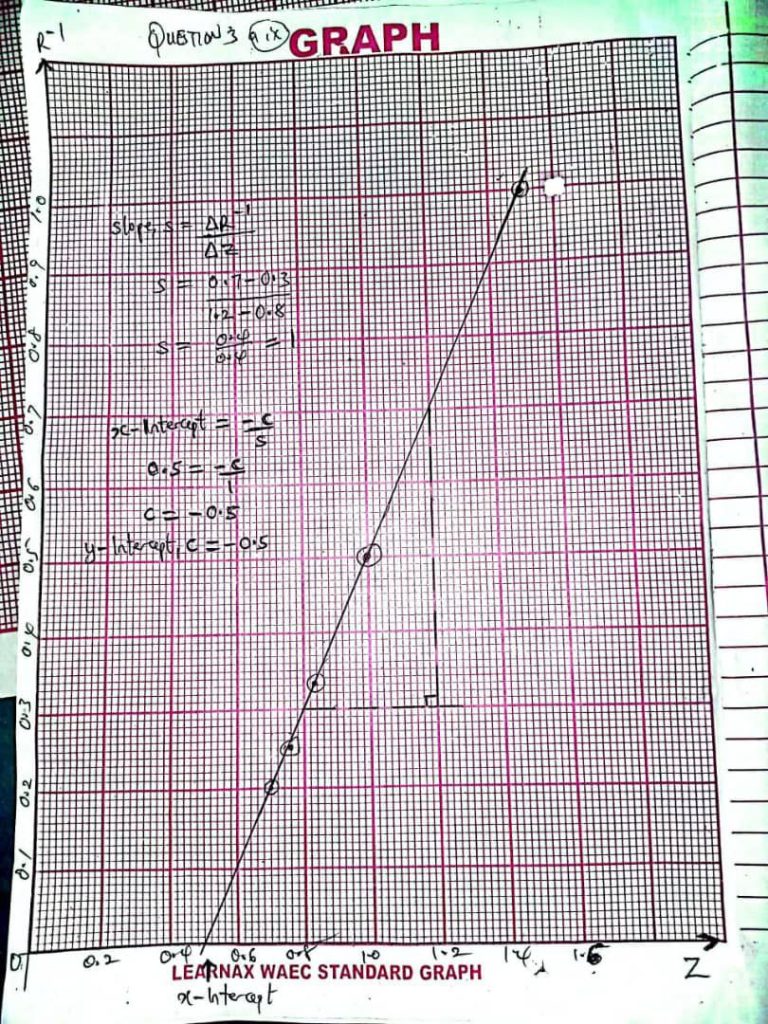

Complete….

Check back soon. We are updating it
Hold on and come back we are working on it
Please help with physics practical answer for tomorrow
Please help with physics practical answer for tomorrow
Pls i beg you post the answer very fast
I am just begging
Check… Now. Still working to complete it
Thank u very much
weldone sir God bless you
Pls I need the complete physics practical answer please
Sir please drop the remaining answers we really need it sir give so you won’t lack and God will bless you for helping others.
Thanks for the info for the physics bough pls post biology obj and theory early and pls quickly complete dis physics or is it completed already
Pls is the physics isn’t complete
It’s complete now. Thank for waiting
It’s complete now. Thank you for waiting
It’s complete now. Thank you
Yes it’s now completed
It’s complete now. Check them out
Thank you… It’s complete now
Thanks bro