Reproduction is a fundamental biological process by which living organisms produce offspring to ensure the survival and continuity of their species. It is one of the key characteristics of life and plays a vital role in passing genetic information from one generation to the next. Whether simple or complex, all living things—from single-celled organisms like bacteria to multicellular organisms like humans—rely on reproduction to sustain their populations and adapt to changing environments. A clear understanding of the meaning and types of reproduction helps explain how life is maintained and transmitted across generations.
In biology, reproduction occurs in two main forms: asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction. Each type has distinct processes, characteristics, and advantages depending on the organism’s structure and habitat. Understanding the meaning and types of reproduction, along with their differences and examples, is essential for grasping the basics of life science, genetics, and evolution. This topic provides a foundation for studying how life continues, evolves, and responds to environmental pressures.
Contents
- Introduction
- Meaning And types of reproduction
- Meaning of sexual reproduction
- Meaning of asexual reproduction
- Differences between sexual and asexual reproduction
- Types of asexual reproduction in animals and examples.
- Conclusion
Meaning and Types of Reproduction
Meaning: Reproduction is the ability of living organisms to give rise to new individuals of the same species. The purpose of reproduction is to ensure the continuity of life.
or
Reproduction is the biological process by which organisms produce offspring, ensuring the continuity of their species. It is one of the fundamental characteristics of living organisms and plays a vital role in the survival and evolution of life on Earth.
Read Also
- Reproductive systems in mammals and their functions
- Reproductive hormones and thier functions in animals
Types of Reproduction in Biology
There are two main types of reproduction in biology. These are asexual and sexual reproduction
1. Asexual reproduction
Meaning: Asexual is the type of reproduction in which new organisms are produced from a single parent without the production of gametes (sex cells). The offspring called the clones are the same in all aspects to each other and to the parent organisms that produce them.
2. Sexual Reproduction
Meaning: Sexual reproduction involves the fusion of the male gametes, e.g, sperm cell and a female gametes, e.g, ova or egg cell to form a zygote which later develops to a young offspring.
Differences between sexual and asexual reproduction
Asexual Reproduction
- One parents involved
- No gametes formed
- Meiosis not involved
- No fertilization/fusion of garments/sex cell/no zygote formed.
- Offspring identical / no genetic variation
- Rapid / faster mode of reproduction
- More individuals are produced
Asexual Reproduction
- Two parents male (and female) involved
- Gametes / sex cell formed
- Meiosis involved
- Fertilization/fusion of gametes / sex cells occurs/zygote formed
- Offspring vary genetically
- Slower mode of reproduction
- Fewer individuals are produced.
Let get clear picture on tabular format
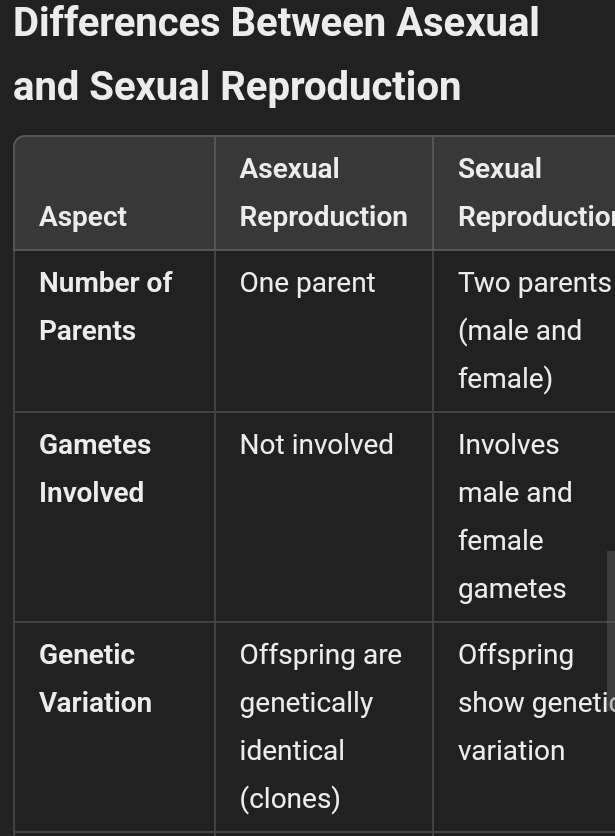
Differences Between sexual and asexual reproduction
| Feature | Asexual Reproduction | Sexual Reproduction |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Parents | One parent involved. | Two parents (male and female) involved. |
| Gamete Formation | No gametes formed. | Gametes (sex cells) are formed. |
| Meiosis Involvement | Meiosis is not involved. | Meiosis is involved. |
| Fertilization | No fertilization/fusion of gametes. | Fertilization/fusion of gametes occurs. |
| Genetic Variation | Offspring are identical (no genetic variation). | Offspring vary genetically. |
| Reproduction Speed | Rapid/faster mode of reproduction. | Slower mode of reproduction. |
| Number of Offspring | More individuals are produced. | Fewer individuals are produced. |
Both forms of reproduction play significant roles in maintaining the balance and diversity of life on Earth.
Types of asexual reproduction in animals
Types of asexual reproduction – examples
- Binary fision – amoeba, paramecium
- Budding – hydra, obelia
- Sporulation – amoeba
- Parthenogenesis – aphids, honey bee
- Schizogony – plasmodium
- Fragmentation – planaria sponges / hydroid coelentetrate.
General Forms of Asexual Reproduction
There are four major forms or method of asexual reproduction. These are binary fission, budding, spore formation and vegetative reproduction.
Conclusion
Reproduction is essential for the continuation of life, ensuring that genetic traits are passed from one generation to the next. By understanding the meaning and types of reproduction, we can better appreciate how organisms grow, adapt, and survive in various environments. Both asexual and sexual reproduction play significant roles in biological diversity and species stability, each offering unique advantages and limitations.
Recognizing the differences between these types of reproduction, along with relevant examples, helps students and researchers understand fundamental life processes. This knowledge forms the basis for more advanced studies in genetics, evolution, medicine, and agriculture, highlighting the importance of reproduction in both natural ecosystems and human development.
Revision Questions for Students
- What is the meaning of reproduction in biology?
- List two main types of reproduction.
- What are the differences between sexual and asexual reproduction?
- List five types of asexual reproduction in animals with one examples each
