Government Past Questions and Answers | JAMB, WAEC, NECO, GCE Theory and Objectives.
Scroll down for COMPLETE QUESTIONS AND ANSWER FOR 2025 NECO GOVERNMENT…

scroll down
Scroll down
scroll down
keep scroll down
scroll down
- Introduction
- 50 Objective Questions with Answers
- 20 Theory Questions
- Exam Preparation Tips
WAEC & NECO Government Past Questions and Answers (Objective and Theory)
Prepare effectively for JAMB, WAEC, GCE and NECO Government past questions exams with this guide featuring 50 multiple-choice questions, 20 theory questions, and expert tips to help you succeed in topics like democracy, constitutions, separation of powers, and public administration.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- 50 WAEC/NECO Government Objective Questions
- Answers to Objective Questions
- 20 WAEC/NECO Government Theory Questions
- Government Exam Preparation Tips
- Conclusion
Introduction
Government is a core subject in the WAEC and NECO syllabus for students in the Arts and Commercial departments. It deals with the study of political institutions, governance systems, public administration, and civic duties. A solid understanding of Government helps students to not only pass their exams but also become active and informed citizens. In this post, you’ll find 50 objective questions and 20 theory questions that reflect commonly tested areas in JAMB, WAEC, GCE and NECO Government exams.
Government Past Questions and Answers | JAMB WAEC, NECO, GCE Theory and Objectives
50 WAEC/NECO Government Objective Questions
- The term “bicameral legislature” means
A. one chamber of parliament
B. two houses of legislature
C. a house with the president and governor
D. two executive arms - The principle of separation of powers was propounded by
A. Aristotle
B. Plato
C. Montesquieu
D. John Locke - A government where the head of state is also the head of government is called a
A. federal system
B. parliamentary system
C. presidential system
D. unitary system - The system of government in which power is shared between central and regional governments is
A. confederation
B. unitary
C. federalism
D. totalitarianism - Universal adult suffrage means
A. all literate citizens can vote
B. all adults have the right to vote
C. only men can vote
D. voting is limited to taxpayers - A bill becomes law after it is
A. discussed in the media
B. signed by the president
C. passed by the judiciary
D. approved by voters - Who ensures discipline in a political party?
A. The press
B. The general public
C. The party whip
D. The police - The constitution of a country can best be described as
A. rules guiding schools
B. military regulations
C. laws of the land
D. traditional customs - The body responsible for conducting elections in Nigeria is
A. ICPC
B. EFCC
C. INEC
D. NJC - Pressure groups influence government policies through
A. legislation
B. strikes and lobbying
C. judicial review
D. military coups - The concept of the rule of law means
A. supremacy of the army
B. immunity for politicians
C. equality before the law
D. power of the president - One disadvantage of a unitary system is
A. duplication of roles
B. weak central government
C. slow decision-making
D. overcentralization - A political party is formed to
A. oppose other parties
B. criticize the military
C. contest elections
D. manage banks - The head of the civil service is known as the
A. clerk
B. chief judge
C. permanent secretary
D. head of service - The process of removing an elected official is called
A. impeachment
B. termination
C. abdication
D. secession - Which organ of government interprets the law?
A. Executive
B. Legislature
C. Judiciary
D. Tribunal - Franchise refers to
A. the right to be appointed
B. the right to vote
C. political campaigns
D. court proceedings - Democracy means
A. rule by the minority
B. rule by judges
C. government by the people
D. military rule - A constitution that can only be amended by a difficult process is called
A. flexible
B. rigid
C. silent
D. partial - Delegated legislation is law made by
A. the courts
B. the president alone
C. individuals
D. subordinate authorities - The 1999 Constitution of Nigeria provides for
A. monarchy
B. military rule
C. democracy
D. communism - The independence of the judiciary means
A. judges can do whatever they like
B. courts are above the law
C. free from executive interference
D. subject to political parties - The first military coup in Nigeria occurred in
A. 1956
B. 1966
C. 1976
D. 1983 - The term “cabinet” refers to
A. all voters in a nation
B. armed forces
C. elected legislators
D. group of ministers - Public corporations are established to
A. compete with private companies
B. generate funds for parties
C. provide essential services
D. replace banks - Nigeria became a republic in
A. 1954
B. 1960
C. 1963
D. 1999 - The two major political parties during the First Republic were
A. APC and PDP
B. AG and NCNC
C. SDP and NRC
D. PRP and APGA - The main function of the legislature is to
A. execute the law
B. interpret the law
C. make laws
D. enforce judgments - A totalitarian government is characterized by
A. political pluralism
B. absence of censorship
C. one-party rule
D. free press - The symbol of national unity in Nigeria is the
A. governor
B. president
C. chief judge
D. inspector general
Government Objective Questions (31–50)
31. A system of government where power is shared between a central authority and its component units is called:
A. Confederalism
B. Federalism
C. Absolutism
D. Totalitarianism
Answer: B
32. The body responsible for making laws in a democratic state is the:
A. Judiciary
B. Executive
C. Legislature
D. Civil Service
Answer: C
33. The principle of separation of powers is associated with:
A. Montesquieu
B. Rousseau
C. Locke
D. Marx
Answer: A
34. Delegated legislation is made by:
A. The electorate
B. The executive only
C. Non-legislative bodies with authority
D. The judiciary
Answer: C
35. One key feature of a unitary system of government is:
A. Multiparty system
B. Concentration of power in the central government
C. Decentralization of power
D. Existence of several constitutions
Answer: B
36. An electoral system where the highest number of votes wins is called:
A. Proportional representation
B. Second ballot
C. Absolute majority
D. Simple majority
Answer: D
37. The rule of law emphasizes:
A. Judicial immunity
B. Equality before the law
C. Arbitrary rule
D. Separation of powers
Answer: B
38. Franchise is best defined as:
A. The right to contest elections
B. The right to vote and be voted for
C. The right to political appointments
D. The right to form political parties
Answer: B
39. A state where the head of state is not a hereditary ruler is known as a:
A. Monarchy
B. Dictatorship
C. Republic
D. Theocracy
Answer: C
40. The pressure group that uses illegal and violent methods is known as:
A. Promotional group
B. Insider group
C. Anomic group
D. Associational group
Answer: C
41. The Green Paper in the law-making process refers to:
A. A proposal for future legislation
B. A bill passed into law
C. A rejected law
D. An emergency decree
Answer: A
42. Which arm of government interprets laws?
A. The legislature
B. The executive
C. The judiciary
D. The civil service
Answer: C
43. A constitution that is not written down in a single document is called a:
A. Flexible constitution
B. Rigid constitution
C. Unwritten constitution
D. Republican constitution
Answer: C
44. Public opinion is mainly measured through:
A. Census
B. Elections
C. Public rallies
D. Opinion polls
Answer: D
45. The highest court in Nigeria is the:
A. High Court
B. Court of Appeal
C. Supreme Court
D. Magistrate Court
Answer: C
46. A major feature of dictatorship is:
A. Existence of opposition
B. Absence of rule of law
C. Supremacy of the judiciary
D. Constitutional supremacy
Answer: B
47. The body that ensures free and fair elections in Nigeria is the:
A. EFCC
B. ICPC
C. INEC
D. NYSC
Answer: C
48. A coup d’état is a method of acquiring power:
A. Legally
B. Through referendum
C. By violent overthrow
D. Through constitutional amendment
Answer: C
49. The principle of checks and balances is essential in:
A. Military regimes
B. Parliamentary systems
C. Democratic systems
D. Feudal systems
Answer: C
50. Civil service neutrality means:
A. Loyalty to political parties
B. Resistance to public opinion
C. Non-involvement in partisan politics
D. Resistance to change
Answer: C
Government Past Questions and Answers | JAMB WAEC, NECO, GCE Theory and Objectives
Answers to Objective Questions
- B
- C
- C
- C
- B
- B
- C
- C
- C
- B
- C
- D
- C
- D
- A
- C
- B
- C
- B
- D
- C
- C
- B
- D
- C
- C
- B
- C
- C
- B
Government Past Questions and Answers | JAMB WAEC, NECO, GCE Theory and Objectives.
2025 government Questions and Answers








NECO 2025 government theory answers


Answer 3. six advantages of public opinion include….
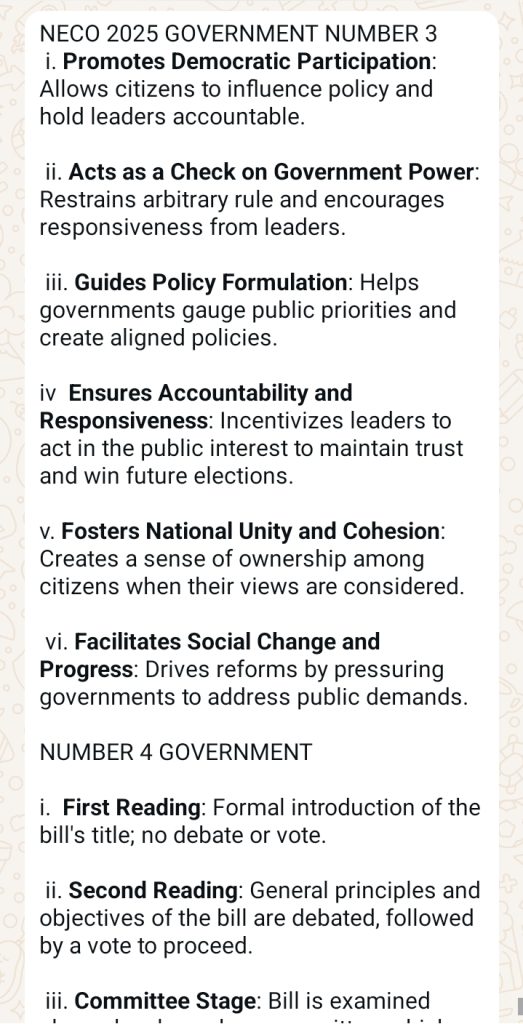
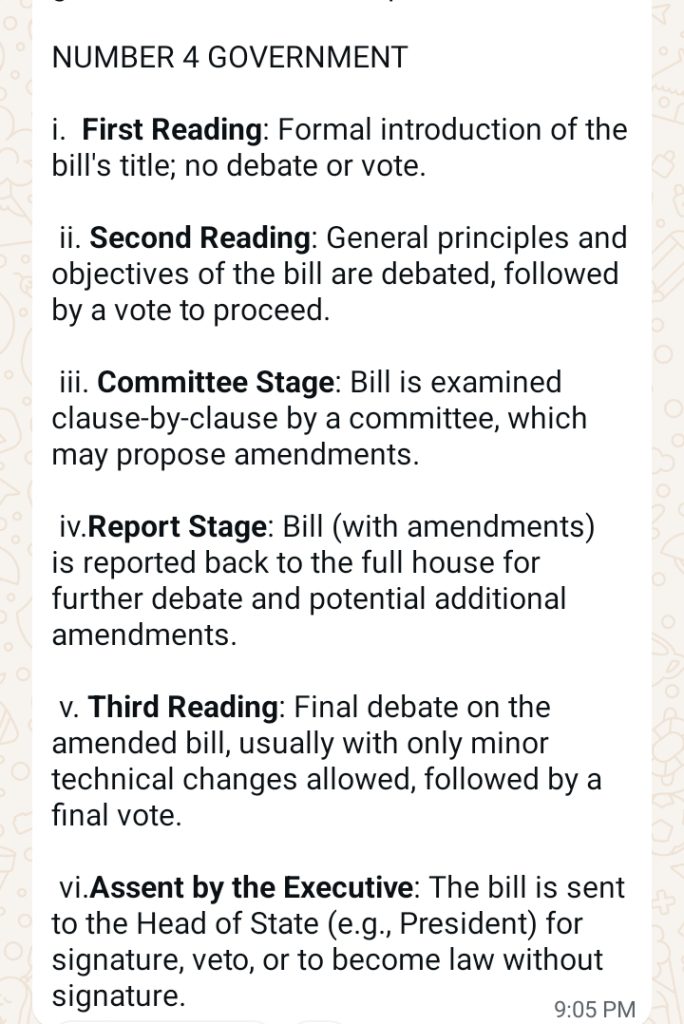
6 stages of Billd
no 6.. provisions of 1999 constitution in Nigeria

No 9. Reasons why local government authorities are created in Nigeria

no 10.. condition for conducting Free and fAir election in Nigeria

2025 GOVERNMENT objectives answers here

20 Government Theory Questions and Answers
- What is a Constitution?
Answer: A constitution is a set of fundamental principles or established precedents that outlines the structure, powers, and functions of government and guarantees the rights and duties of citizens in a state. - Describe two types of Constitution.
Answer:- Written Constitution: Formally documented and codified, like Nigeria’s 1999 Constitution.
- Unwritten Constitution: Based on customs, traditions, and legal judgments, such as the British constitution.
- State five features of a Federal System.
Answer:- Power sharing between central and state governments
- Supremacy of the constitution
- Existence of multiple tiers of government
- Independent judiciary
- Written and rigid constitution
- Explain the Rule of Law.
Answer: The Rule of Law means that every individual, regardless of status, is subject to the law and that legal equality and fairness are guaranteed under a functioning judicial system. - Define Democracy.
Answer: Democracy is a system of government in which power belongs to the people, either directly or through elected representatives, with regular, free, and fair elections. - Mention three types of Political Culture.
Answer:- Parochial – Low political awareness and participation
- Subject – Some awareness but little participation
- Participant – High awareness and active participation in politics
- Highlight four functions of the Legislature.
Answer:- Making laws
- Oversight of the executive
- Approval of budgets
- Ratification of appointments and treaties
- Define Political Socialization.
Answer: Political socialization is the process through which individuals acquire political values, attitudes, norms, and knowledge about the political system. - State three functions of Political Parties.
Answer:- Nomination of candidates for elections
- Formulation of public policies
- Mobilization of public opinion and education of voters
- What are Pressure Groups?
Answer: Pressure groups are organized groups that seek to influence government policies and decisions without contesting elections themselves. - Define Citizenship.
Answer: Citizenship is the legal status of being a recognized member of a state, with specific rights and obligations under the law. - Mention three ways of acquiring Citizenship.
Answer:- By Birth – Born to parents who are citizens
- By Registration – Through legal application and approval
- By Naturalization – Acquiring citizenship after fulfilling residence and legal requirements
- State four duties of a Citizen.
Answer:- Obedience to laws
- Payment of taxes
- Participation in civic duties (e.g., voting)
- Defense of the nation
- Explain the principle of Separation of Powers.
Answer: Separation of Powers is a political doctrine that divides governmental powers among the legislative, executive, and judicial arms to prevent abuse and ensure checks and balances. - List the three arms of Government and their functions.
Answer:- Legislature – Law-making
- Executive – Implementation of laws and policies
- Judiciary – Interpretation of laws and resolution of disputes
- Describe Military Rule.
Answer: Military rule is a form of governance in which the armed forces seize and control political power, usually through a coup d’état, often suspending democratic structures and the constitution. - What is a Unitary System?
Answer: A unitary system is a form of government where all powers are concentrated in a single central authority, with little or no autonomy for sub-national units. - Highlight four features of a Parliamentary System.
Answer:- Fusion of executive and legislative functions
- Head of government is the Prime Minister
- Collective cabinet responsibility
- Possibility of removal of government via a vote of no confidence
- State the composition of the Nigerian Judiciary.
Answer: The Nigerian judiciary consists of the Supreme Court, Court of Appeal, Federal and State High Courts, Customary Courts, Sharia Courts, and other specialized courts. - What is the significance of Local Government in Nigeria?
Answer: Local government promotes grassroots development, ensures political participation at the local level, provides essential services, and acts as a training ground for national leadership.
20 WAEC/NECO Government Theory Questions
- Define government and mention three of its characteristics.
- Explain the concept of separation of powers and its advantages.
- Highlight four differences between a presidential and a parliamentary system.
- What are the functions of the executive arm of government?
- List and explain any five sources of a constitution.
- Define public opinion and discuss its importance in a democratic society.
- Write short notes on political party and pressure group.
- Outline the merits and demerits of a federal system.
- Describe three methods by which citizens can control government.
- What are the limitations to the rule of law in Nigeria?
- State the features of a unitary system of government.
- Mention the duties of local government authorities in Nigeria.
- What is delegated legislation? State two advantages and two disadvantages.
- Explain the role of INEC in Nigerian elections.
- Identify and explain any four fundamental human rights.
- Describe the functions of the legislature in Nigeria.
- What are the causes of military intervention in politics?
- Differentiate between civil service and public service.
- State the major challenges of democracy in West Africa.
- Explain the concept of citizenship and how it can be acquired in Nigeria.
Government Past Questions and Answers | JAMB WAEC, NECO, GCE Theory and Objectives
Government Exam Preparation Tips
- Study and understand the current constitution of Nigeria.
- Practice multiple past questions across WAEC and NECO years.
- Make summary notes of key concepts like democracy, organs of government, rule of law, and electoral systems.
- Learn historical dates of major political events in Nigeria.
- Practice writing concise answers to theory questions under timed conditions.
READ ALSO – English literature past questions and answers | JAMB, WAEC, NECO, GCE
Conclusion
Government is a subject that rewards students who master both theory and practical political events. With these 50 objective questions and 20 theory questions, you now have a powerful revision tool for the WAEC, NECO and JAMB Government exams. Use this questions to assess your knowledge, identify weak spots, and focus your reading. You will pass your exam wish you the best..
