Mastering Geography Past Questions and Answers with objectives for WAEC, NECO and JAMB
Scroll down down to 2025 HUMAN GEOGRAPHY ESSAY AND OBJECTIVES ANSWERS printed papers
Scroll down down to 2025 HUMAN GEOGRAPHY ESSAY AND OBJECTIVES ANSWERS
scroll down for today paper
scroll down
scroll down
scroll down to today’s paper
scroll down
Geography is a fascinating subject that studies the earth, its physical features, climate, and human activities. For students preparing for WAEC (West African Examinations Council) and JAMB (Joint Admissions and Matriculation Board) exams, Geography can be one of the most rewarding subjects if approached correctly. One of the best ways to excel in this subject is by practicing past questions and answers.
In this hall, we’ll highlight the importance of Geography past questions and answers, strategies for using them effectively, with 100 Objectives and 100 theories past questions and answers
Importance of Studying Geography Past Questions and Answers?
- Familiarity with Exam Format:
Geography past questions help you understand the structure of WAEC and JAMB exams, including how questions are framed, the marking scheme, and the expected level of detail in your answers. - Identifying Frequently Tested Topics:
Exam bodies often repeat questions from key topics. By studying past questions, you’ll notice recurring areas such as map reading, climatic zones, and population studies. - Improving Speed and Accuracy:
Regular practice with past questions allows you to answer faster and more accurately during the actual exam. - Boosting Confidence:
Knowing what to expect can significantly reduce exam anxiety and build confidence in your preparation.
Tips for Excelling in Geography Past Questions and Answers for WAEC/JAMB
Let me show you some tips for excelling in either WAEC or JAMB geography.
- Focus on frequently tested topics like map work, climatic zones, and economic geography.
- Use diagrams and maps to enhance your answers where necessary.
- Review past questions and answers repeatedly to reinforce your understanding.
- Develop strong map-reading skills to excel in practical Geography.
- Manage your time effectively during the exam to answer all questions.
Mastering Geography Past Questions and Answers for WAEC and JAMB requires consistent practice and a clear understanding of the subject’s core concepts. By leveraging past questions and answers, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of the exam format, improve your confidence, and increase your chances of success.
Read Also
- Biology Past Questions and Answers for WAEC/JAMB
- Chemistry Past Questions and Answers for WAEC and JAMB
- Physics past Questions and Answers for WAEC/JAMB
100 Geography Past Questions and answers from WAEC, NECO, GCE, and JAMB past questions, each with options and the correct answers provided
Geography Past Questions and answers (1–100)
1. The Earth is spherical in shape because
A. it casts a circular shadow on the moon
B. it is covered with water
C. it is the largest planet
D. of gravitational pull
Answer: A
2. Lines of latitude are
A. equal in length
B. not parallel to each other
C. measured eastwards
D. parallel to the equator
Answer: D
3. The longest latitude is
A. Tropic of Capricorn
B. Arctic Circle
C. Equator
D. Tropic of Cancer
Answer: C
4. The instrument used to measure humidity is
A. Thermometer
B. Hygrometer
C. Barometer
D. Anemometer
Answer: B
5. A scale of 1:50,000 means that
A. 1 unit represents 50,000 units on the map
B. 1 unit on the ground equals 50,000 units on the map
C. The area is 50,000 square km
D. 1 inch equals 50,000 meters
Answer: A
6. Which of the following is not an agent of erosion?
A. Wind
B. Glacier
C. Volcano
D. River
Answer: C
7. All are features of a youthful river except
A. Rapids
B. Waterfalls
C. Meanders
D. Gorges
Answer: C
8. Fold mountains are formed by
A. volcanic activities
B. earth tremors
C. compressional forces
D. erosional activities
Answer: C
9. The direction of prevailing wind is recorded with a
A. Wind vane
B. Anemometer
C. Barometer
D. Thermometer
Answer: A
10. The sun appears to rise in the east and set in the west because of
A. the rotation of the Earth
B. the orbit of the Earth
C. the shape of the Earth
D. refraction
Answer: A
11. The atmosphere is made up of all the following gases except
A. Oxygen
B. Nitrogen
C. Carbon dioxide
D. Chlorine
Answer: D
12. Which layer of the Earth lies beneath the crust?
A. Lithosphere
B. Mantle
C. Core
D. Troposphere
Answer: B
13. Isobars are lines that join places of equal
A. rainfall
B. temperature
C. pressure
D. altitude
Answer: C
14. A rain shadow is formed when
A. clouds are heavy
B. wind descends the leeward side
C. wind rises the windward slope
D. it rains on both sides
Answer: B
15. Which of these countries is landlocked?
A. Nigeria
B. Ethiopia
C. Ghana
D. Kenya
Answer: B
16. What is the local time of a place on longitude 45°E when the GMT is 12 noon?
A. 3:00 am
B. 3:00 pm
C. 9:00 am
D. 9:00 pm
Answer: B
17. What type of vegetation is found in the Congo Basin?
A. Mangrove
B. Desert
C. Tropical rainforest
D. Montane forest
Answer: C
18. The least populated continent is
A. Africa
B. Asia
C. Europe
D. Australia
Answer: D
19. Which of the following is a volcanic mountain?
A. Everest
B. Kilimanjaro
C. Atlas
D. Himalayas
Answer: B
20. Deserts are mainly found around
A. the Equator
B. the Tropics
C. the Arctic
D. high mountains
Answer: B
21. Which country is the largest in Africa by land area?
A. Egypt
B. South Africa
C. Nigeria
D. Algeria
Answer: D
22. A bay is best described as
A. an inland sea
B. a narrow channel of water
C. a broad curve in a coastline
D. a mountain near the sea
Answer: C
23. A drainage basin refers to
A. an area of land covered by lakes
B. land covered by glaciers
C. land drained by a river and its tributaries
D. a machine-made canal
Answer: C
24. What type of rainfall is common in tropical rainforests?
A. Relief
B. Convectional
C. Cyclonic
D. Orographic
Answer: B
25. Which ocean is the largest in the world?
A. Atlantic
B. Indian
C. Pacific
D. Arctic
Answer: C
26. A cliff is formed by
A. volcanic eruption
B. deposition
C. coastal erosion
D. deforestation
Answer: C
27. Which of these is not a method of population census?
A. De jure
B. De facto
C. Estimation
D. Remote sensing
Answer: D
28. The Sahara desert is mainly found in
A. West Africa
B. Central Africa
C. North Africa
D. Southern Africa
Answer: C
29. The Equator is located at
A. 0° longitude
B. 180° latitude
C. 0° latitude
D. 90° latitude
Answer: C
30. The main cause of desertification is
A. irrigation
B. deforestation
C. afforestation
D. migration
Answer: B
31. The most populous country in Africa is
A. South Africa
B. Nigeria
C. Egypt
D. Ethiopia
Answer: B
32. A delta is formed at the
A. middle course of a river
B. upper course of a river
C. mouth of a river
D. source of a river
Answer: C
33. The type of settlement that develops along a road is called
A. Nucleated
B. Linear
C. Dispersed
D. Cluster
Answer: B
34. An ox-bow lake is formed by
A. glacial erosion
B. wave action
C. meandering river
D. coastal deposition
Answer: C
35. Which of these is a renewable resource?
A. Crude oil
B. Natural gas
C. Forest
D. Coal
Answer: C
36. Longitude 0° is called
A. Greenwich Meridian
B. Equator
C. Prime Equator
D. International Date Line
Answer: A
37. The boundary between two drainage basins is called a
A. river divide
B. interfluve
C. basin margin
D. watershed
Answer: D
38. Which of the following is a highland in Nigeria?
A. Mambilla Plateau
B. Chad Basin
C. Sokoto Plain
D. Cross River Basin
Answer: A
39. Which of these is not a layer of the Earth’s atmosphere?
A. Troposphere
B. Lithosphere
C. Mesosphere
D. Stratosphere
Answer: B
40. The smallest planet in the solar system is
A. Earth
B. Pluto
C. Mercury
D. Mars
Answer: C
41. A rift valley is formed by
A. compressional forces
B. faulting
C. folding
D. volcanic eruption
Answer: B
42. The scale 1cm to 5km on a map is a
A. linear scale
B. statement scale
C. fractional scale
D. verbal scale
Answer: B
43. The major occupation of people in delta regions is
A. fishing
B. mining
C. trading
D. farming
Answer: A
44. The major export of Nigeria is
A. Palm oil
B. Cocoa
C. Petroleum
D. Cotton
Answer: C
45. Which of the following zones supports nomadic herding?
A. Mangrove swamp
B. Rainforest
C. Sahel savanna
D. Midland belt
Answer: C
46. Which map feature shows relief?
A. Symbols
B. Compass
C. Contour lines
D. Grid lines
Answer: C
47. Which of the following is a product of volcanic eruption?
A. Sandstone
B. Limestone
C. Lava
D. Shale
Answer: C
48. The two main types of migration are
A. voluntary and involuntary
B. old and new
C. long and short
D. internal and external
Answer: D
49. Which of these is a conurbation in Nigeria?
A. Zaria
B. Ibadan
C. Lagos
D. Ilorin
Answer: C
50. Which of the following is a human factor affecting agriculture?
A. Rainfall
B. Temperature
C. Soil type
D. Land tenure
Answer: D
Geography Past Questions and answers on objectives (51–100) from WAEC, NECO, GCE, and JAMB past questions.
51. Which of these is a major cause of soil erosion?
A. Terracing
B. Overgrazing
C. Afforestation
D. Mulching
Answer: B
52. The deflection of wind due to the rotation of the Earth is known as
A. cyclonic effect
B. centrifugal force
C. coriolis force
D. gravity
Answer: C
53. The process of weathering involving the repeated freezing and thawing of water is called
A. chemical weathering
B. exfoliation
C. frost action
D. oxidation
Answer: C
54. A good example of a rift valley lake is
A. Lake Chad
B. Lake Victoria
C. Lake Tanganyika
D. Lake Volta
Answer: C
55. The soil type most suitable for agriculture is
A. laterite
B. sandy soil
C. loamy soil
D. clay soil
Answer: C
56. What is the major source of energy in Nigeria?
A. Natural gas
B. Coal
C. Petroleum
D. Hydro-power
Answer: C
57. The climate experienced in the Mediterranean region is
A. hot and wet all year round
B. dry summers and wet winters
C. very cold and dry
D. warm and humid all year
Answer: B
58. The vegetation found in areas with rainfall between 250mm and 500mm is
A. desert
B. rainforest
C. savanna
D. mangrove
Answer: A
59. Which of these instruments is used to determine wind speed?
A. Anemometer
B. Hygrometer
C. Rain gauge
D. Barometer
Answer: A
60. Earthquakes are caused by
A. glacial movement
B. folding and faulting
C. rainfall
D. volcanic ash
Answer: B
61. Which of the following rocks is igneous?
A. Marble
B. Granite
C. Limestone
D. Shale
Answer: B
62. A major tributary of River Niger is
A. River Benue
B. River Zambezi
C. River Nile
D. River Limpopo
Answer: A
63. The longest river in Africa is
A. River Congo
B. River Niger
C. River Nile
D. River Benue
Answer: C
64. Which of these is a natural resource?
A. Textile
B. Crude oil
C. Plastics
D. Fertilizer
Answer: B
65. The part of the Earth where life exists is called
A. troposphere
B. crust
C. biosphere
D. mantle
Answer: C
66. A lagoon is best described as
A. a river mouth
B. a shallow coastal lake
C. an inland lake
D. a delta
Answer: B
67. The primary economic activity is
A. retailing
B. banking
C. farming
D. transportation
Answer: C
68. The shortest route from West Africa to Europe is through
A. the Mediterranean Sea
B. the Sahara Desert
C. the Red Sea
D. the Suez Canal
Answer: A
69. Which of these is a benefit of contour ploughing?
A. Water pollution
B. Soil erosion
C. Soil conservation
D. Bush burning
Answer: C
70. Which of these rivers is a boundary between Nigeria and Cameroon?
A. River Niger
B. River Benue
C. River Ogun
D. Cross River
Answer: D
71. The process of wind-blown sand striking rock surfaces and wearing them away is called
A. exfoliation
B. abrasion
C. deflation
D. attrition
Answer: B
72. Which of these features is formed by glacial erosion?
A. Delta
B. Cirque
C. Sand dune
D. Ox-bow lake
Answer: B
73. The atmospheric layer that contains the ozone layer is
A. troposphere
B. stratosphere
C. mesosphere
D. thermosphere
Answer: B
74. The point on the Earth’s surface vertically above the focus of an earthquake is called
A. epicenter
B. fault line
C. origin
D. volcano
Answer: A
75. Which of the following is a conservative method of fishing?
A. Use of explosives
B. Use of fish traps
C. Poisoning
D. Trawling
Answer: B
76. The major factor influencing the location of iron and steel industry is
A. proximity to market
B. power supply
C. raw materials
D. labor supply
Answer: C
77. Which of the following is a feature of a developing country?
A. High life expectancy
B. Low literacy level
C. High industrial output
D. Efficient infrastructure
Answer: B
78. River capture is caused by
A. earthquake
B. rejuvenation
C. meandering
D. river piracy
Answer: D
79. The movement of people from rural to urban areas is called
A. urbanization
B. emigration
C. rural depopulation
D. rural-urban migration
Answer: D
80. Which of the following is an effect of deforestation?
A. Reforestation
B. Erosion
C. Mulching
D. Windbreak
Answer: B
81. What is the capital of the world’s largest country by area?
A. Beijing
B. Moscow
C. Washington
D. Ottawa
Answer: B
82. Lines joining places of equal temperature are known as
A. isohyets
B. isobars
C. isotherms
D. isohels
Answer: C
83. The process of removing salt from seawater is called
A. salinization
B. desalination
C. distillation
D. filtration
Answer: B
84. The natural region that supports lumbering is
A. Mediterranean
B. Equatorial
C. Temperate forest
D. Sahel
Answer: C
85. Which of these is a major import of Nigeria?
A. Petroleum
B. Machinery
C. Cocoa
D. Groundnut
Answer: B
86. The natural vegetation of the Nile Delta is
A. mangrove swamp
B. desert shrubs
C. papyrus and reeds
D. bamboo
Answer: C
87. The mouth of a river with many distributaries is called a
A. delta
B. gorge
C. basin
D. estuary
Answer: A
88. One of the following is not an effect of urbanization
A. pollution
B. traffic congestion
C. unemployment
D. desertification
Answer: D
89. The first layer of the Earth’s interior is
A. crust
B. mantle
C. core
D. lithosphere
Answer: A
90. The most important factor determining climate is
A. ocean currents
B. altitude
C. latitude
D. winds
Answer: C
91. River Niger enters the Atlantic Ocean through
A. an estuary
B. a delta
C. a lagoon
D. a gorge
Answer: B
92. Which of these countries has no international boundary with Nigeria?
A. Chad
B. Benin
C. Ghana
D. Niger
Answer: C
93. The major occupation in the Sahel savanna is
A. fishing
B. nomadic herding
C. mining
D. crop farming
Answer: B
94. Which country in Africa has the highest population?
A. Egypt
B. Ethiopia
C. Nigeria
D. DR Congo
Answer: C
95. The direction of a place from another using the cardinal points is called
A. latitude
B. bearing
C. relative location
D. longitude
Answer: C
96. Limestone is mainly used for
A. roofing
B. glass production
C. cement production
D. fertilizer
Answer: C
97. The largest desert in the world is the
A. Kalahari
B. Gobi
C. Sahara
D. Atacama
Answer: C
98. The change in temperature with height is called
A. temperature drop
B. lapse rate
C. inversion
D. stratification
Answer: B
99. Which is the most industrialized region in Nigeria?
A. North West
B. South East
C. South West
D. North East
Answer: C
100. The major cash crop of the forest zone of Nigeria is
A. Millet
B. Cocoa
C. Sorghum
D. Cotton
Answer: B
Theory Section
List of 100 Geography past questions and answers grouped into key topics to help you prepare effectively for WAEC, NECO and JAMB.
1. PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY
- What are the three main types of rocks?
Answer: Igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. - What type of rock is formed from cooling magma?
Answer: Igneous rocks. - Which process is responsible for the formation of sedimentary rocks?
Answer: Deposition and compaction of sediments. - What is the major cause of desertification in West Africa?
Answer: Overgrazing, deforestation, and climate change. - Define weathering.
Answer: The breakdown of rocks into smaller particles by physical, chemical, or biological processes. - What is a delta?
Answer: A landform created at the mouth of a river where it deposits sediments. - What are the three types of rainfall?
Answer: Convectional, orographic, and cyclonic rainfall. - Name two features of a limestone region.
Answer: Caves and sinkholes. - What is a rain shadow?
Answer: A dry area on the leeward side of a mountain where precipitation is reduced. - What is the main cause of ocean currents?
Answer: Wind, the Earth’s rotation, and differences in water density.
2. HUMAN GEOGRAPHY
- What is population density?
Answer: The number of people per unit area of land. - Name two factors that influence population distribution.
Answer: Climate and availability of resources. - What is urbanization?
Answer: The growth of towns and cities as people move from rural to urban areas. - What is migration?
Answer: The movement of people from one place to another. - Define rural settlement.
Answer: A settlement with a low population density, primarily engaged in agriculture. - List two advantages of urbanization.
Answer: Improved infrastructure and better access to social services. - What are push factors in migration?
Answer: Factors that force people to leave an area, such as poverty or conflict. - Name two types of economic activities.
Answer: Primary (farming) and secondary (manufacturing). - What is the difference between renewable and non-renewable resources?
Answer: Renewable resources can be replenished, while non-renewable resources cannot. - What is the role of transportation in economic development?
Answer: It facilitates the movement of goods and people.
3. REGIONAL GEOGRAPHY (NIGERIA AND AFRICA)
- Name two major rivers in Nigeria.
Answer: River Niger and River Benue. - What is the main vegetation type in northern Nigeria?
Answer: Sudan savanna. - List two mineral resources found in Nigeria.
Answer: Crude oil and limestone. - What is the largest desert in Africa?
Answer: The Sahara Desert. - Name two countries in West Africa.
Answer: Ghana and Senegal. - What is the major occupation in the savanna region?
Answer: Cattle rearing and crop farming. - What is the primary export of Nigeria?
Answer: Crude oil. - Which African river is known as the “father of African rivers”?
Answer: River Nile. - What is the climate of the equatorial region?
Answer: Hot and wet throughout the year. - Name one national park in Nigeria.
Answer: Yankari National Park.
4. PRACTICAL GEOGRAPHY
- What is a topographic map?
Answer: A map that shows the physical features of an area using contour lines. - What do contour lines represent on a map?
Answer: Areas of equal elevation. - What is the scale of a map?
Answer: The ratio between a distance on the map and the actual distance on the ground. - What does a blue color on a map typically represent?
Answer: Water bodies. - How is distance measured on a map?
Answer: Using the map scale. - What is a compass used for?
Answer: Determining direction. - What is latitude?
Answer: The distance north or south of the equator, measured in degrees. - What is longitude?
Answer: The distance east or west of the prime meridian, measured in degrees. - What are grid references used for?
Answer: Locating specific points on a map. - Name the four cardinal points.
Answer: North, South, East, and West.
5. CLIMATOLOGY AND VEGETATION
- What is the difference between weather and climate?
Answer: Weather is the short-term condition of the atmosphere, while climate is the average weather over a long period. - Name two instruments used to measure weather.
Answer: Thermometer and barometer. - What is a tropical rainforest?
Answer: A dense forest found in areas with high rainfall and high temperatures. - What is the harmattan?
Answer: A dry, dusty wind that blows from the Sahara during the dry season. - What is the main cause of rainfall?
Answer: Condensation of water vapor in the atmosphere. - Define savanna vegetation.
Answer: Grassland with scattered trees, found in tropical and subtropical regions. - What is the main characteristic of desert vegetation?
Answer: Plants adapted to survive in dry conditions. - Which region experiences Mediterranean climate?
Answer: Southern Europe and parts of North Africa. - What is a deciduous forest?
Answer: A forest where trees shed their leaves seasonally. - What is the importance of vegetation?
Answer: It provides oxygen, regulates climate, and prevents soil erosion.
ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS
- What is the Greenwich Meridian?
Answer: The prime meridian, located at 0° longitude. - Name two examples of renewable resources.
Answer: Solar energy and wind energy. - What is the major cause of flooding in urban areas?
Answer: Poor drainage systems. - What are relief features?
Answer: The physical features of the earth’s surface, such as mountains and valleys. - What is the Coriolis effect?
Answer: The deflection of winds due to the Earth’s rotation.
6. ADVANCED CLIMATOLOGY AND ATMOSPHERIC STUDIES
- What is the ozone layer?
Answer: A layer in the Earth’s stratosphere that absorbs most of the sun’s ultraviolet radiation. - What are isobars?
Answer: Lines on a weather map connecting points of equal atmospheric pressure. - Define humidity.
Answer: The amount of water vapor in the atmosphere. - What is the difference between absolute and relative humidity?
Answer: Absolute humidity is the actual amount of water vapor in the air, while relative humidity is the percentage of water vapor relative to the air’s capacity. - Name two causes of global warming.
Answer: Deforestation and the burning of fossil fuels. - What is a cyclone?
Answer: A large system of winds rotating inward to an area of low atmospheric pressure. - What are the characteristics of a Mediterranean climate?
Answer: Hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. - What is the main characteristic of the equatorial climate?
Answer: High temperatures and high rainfall throughout the year. - What is a monsoon?
Answer: A seasonal wind that brings heavy rainfall to certain regions, particularly in South Asia. - What is a temperature inversion?
Answer: A reversal of the normal decrease in temperature with altitude.
7. ECONOMIC AND AGRICULTURAL GEOGRAPHY
- What is subsistence farming?
Answer: Farming that provides food primarily for the farmer’s family. - Define mixed farming.
Answer: A farming system that combines crop cultivation with livestock rearing. - What is crop rotation?
Answer: The practice of growing different crops on the same land in successive seasons to maintain soil fertility. - Name two major cash crops grown in Nigeria.
Answer: Cocoa and oil palm. - What is irrigation?
Answer: The artificial application of water to crops. - What is the Green Revolution?
Answer: A period when agriculture was modernized through the use of high-yielding seeds, fertilizers, and irrigation. - List two disadvantages of deforestation.
Answer: Loss of biodiversity and increased soil erosion. - What is the main benefit of agroforestry?
Answer: It helps conserve soil and improve biodiversity while producing crops. - What is the significance of trade in economic geography?
Answer: Trade facilitates the exchange of goods and services and promotes economic growth. - Name two modes of transport used in trade.
Answer: Road and maritime transport.
8. MAP READING AND INTERPRETATION
- What is a choropleth map?
Answer: A map that uses shading or colors to represent data density in specific areas. - What is an atlas?
Answer: A collection of maps. - Define scale in map reading.
Answer: The relationship between a distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground. - What is a geographic information system (GIS)?
Answer: A computer-based tool used for mapping and analyzing spatial data. - What is the significance of map symbols?
Answer: They represent various features on a map, such as rivers, roads, and settlements. - What is relief on a map?
Answer: The representation of the physical features of the land surface. - What do vertical lines on a map represent?
Answer: Longitudes. - What is a contour interval?
Answer: The vertical distance between two consecutive contour lines. - What does a green color on a map typically represent?
Answer: Vegetation or forested areas. - What is the function of a key or legend on a map?
Answer: To explain the meaning of symbols used on the map.
9. ENVIRONMENTAL GEOGRAPHY
- What is environmental degradation?
Answer: The deterioration of the environment through depletion of resources, pollution, or destruction of ecosystems. - Name two types of pollution.
Answer: Air pollution and water pollution. - What is biodiversity?
Answer: The variety of life in an ecosystem. - What are natural resources?
Answer: Resources that occur naturally in the environment, such as water, forests, and minerals. - What is sustainable development?
Answer: Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet theirs. - What is afforestation?
Answer: Planting trees in areas where there were no previous forests. - List two effects of oil spillage.
Answer: Soil infertility and water pollution. - What is desertification?
Answer: The process by which fertile land becomes desert due to drought or human activities. - What is an ecosystem?
Answer: A community of living organisms interacting with their physical environment. - Name two causes of water pollution.
Answer: Industrial waste and agricultural runoff.
10. TIME AND EARTH’S MOTION
- What is the shape of the Earth?
Answer: An oblate spheroid. - What is the significance of the International Date Line?
Answer: It separates two consecutive calendar days. - What causes day and night?
Answer: The rotation of the Earth on its axis. - How many time zones are there on Earth?
Answer: 24 time zones. - What is the duration of one Earth’s revolution around the sun?
Answer: Approximately 365.25 days.
These 100 Geography Past questions and answers with theory are for WAEC, NECO, GCE and JAMB preparation.
2025 NECO human geography
2025 NECO ON HUMAN GEOGRAPHY QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS


2025 NECO GEOGRAPHY ESSAY ANSWERS
6 (a)
Cottage industry refers to a small-scale, home-based production of goods using traditional methods and tools. These industries are often operated by individuals or families and do not involve large amounts of capital or machinery. Examples include weaving, pottery, blacksmithing, and local soap making.
6 (b) i
i. Textile cottage industry: This involves the production of fabrics, clothing, and traditional attire such as Aso Oke or Ankara using local looms or sewing machines. It is typically run by skilled tailors and weavers who create designs suited to local tastes and culture.
ii. Leather cottage industry: In areas like Kano and Sokoto, craftsmen process animal hides into usable items like shoes, belts, and bags using age-old techniques. These products are sold locally and sometimes exported, contributing to rural incomes and cultural preservation.
6 (b) ii
i. Cottage industries use local raw materials such as cotton, clay, or hides which are easily accessible and affordable.
ii. They require low capital investment since production tools and facilities are minimal and often handcrafted.
iii. Production is carried out within homes or small workshops, allowing people to combine domestic responsibilities with economic activity.
iv. Labour is usually provided by family members, which helps reduce operating costs and ensures skill transfer across generations.
6 (c)
i. Industries are located in rural areas due to the easy availability of raw materials such as agricultural produce, hides, and clay which are sourced locally without transport costs.
ii. Land in rural areas is more affordable and available compared to urban zones, allowing these industries to establish workshops or storage facilities without high expenses.
ANSWERS
COMPLETE 1-6 NECO HUMAN AND REGIONAL GEOGRAPHY
NUMBER ONE
(1a)
Population refers to the total number of people living in a particular geographical area at a specific time. It includes all individuals regardless of age, gender, or status.
(1bi)
Size: Population size refers to the total number of people in a country or region. It indicates how large or small a population is and is usually determined through a census. The size affects the demand for goods, services, resources, and infrastructure in an area. A large population may mean a large labor force and market, while a small population may limit economic growth.
(1bii)
Density: Population density is the number of people living per unit area, typically per square kilometer or mile. It is calculated by dividing the population size by the land area. High population density may lead to overcrowding, pressure on social amenities, and environmental degradation, while low density may indicate under-utilization of resources and services.
(1biii)
Quality: Population quality refers to the characteristics that determine how productive or effective the population is. It includes aspects such as health, education, skills, and general well-being of the people. A high-quality population contributes positively to the development of a nation through a skilled and healthy workforce.
(1c)
(PICK ANY THREE)
(i) Level of education
(ii) Availability of healthcare services
(iii) Nutrition and feeding
(iv) Housing and living conditions
(v) Employment opportunities
(vi) Environmental sanitation and hygiene
NECO HUMAN AND REGIONAL GEOGRAPHY
NUMBER TWO
(2a)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) Zuma Rock
(ii) Gurara Waterfalls
(iii) Farin Ruwa Falls
(iv) Assop Falls
(v) Jos Wildlife Park
(vi) National Museum, Jos
(vii) Mount Patti
(viii) Lord Lugard’s Residence
(2b)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) Source of Revenue Generation: Tourism is a major contributor to national income. It brings in foreign exchange from international tourists who spend on accommodation, transportation, food, and souvenirs. Local governments also earn through taxes, entry fees, and levies on tourism-related services. This revenue can be reinvested into other sectors like health, education, and infrastructure.
(ii) Employment Opportunities: Tourism creates direct and indirect jobs for the population. Direct employment can be found in hotels, travel agencies, tour operations, and museums. Indirectly, people also earn income by producing and selling crafts, providing transport services, and supplying food. This reduces the unemployment rate and improves the standard of living.
(iii) Infrastructure Development: To attract and accommodate tourists, governments and private investors often improve infrastructure such as roads, airports, hotels, communication networks, and recreational facilities. These developments do not only benefit tourists but also enhance the quality of life for the local population and open up remote areas to more opportunities.
(iv) Cultural Preservation and Awareness: Tourism encourages the preservation of a nation’s culture and heritage. Traditional festivals, historical sites, monuments, and artifacts are maintained and promoted as tourist attractions. This also helps to educate both locals and foreigners about the cultural history, customs, and values of different communities, thereby fostering national pride and identity.
(v) Foreign Investment Attraction: A vibrant tourism industry can attract foreign investors who may be interested in building hotels, resorts, transportation networks, and entertainment centers. These investments not only boost economic growth but also lead to technology transfer and skill development among locals, thereby stimulating other sectors of the economy.
(vi) Promotion of International Peace and Diplomacy: Tourism serves as a means of cultural exchange, allowing people from different countries to interact and understand each other’s ways of life. This promotes tolerance, mutual respect, and global peace. It also strengthens diplomatic ties and fosters cooperation between countries, especially those that share tourism interests.
(2c)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) Improvement of security in tourist areas
(ii) Development of infrastructure (roads, power, water)
(iii) Promotion and marketing of tourist sites locally and internationally
(iv) Enacting favorable tourism policies and regulations
(v) Training and capacity building for tourism professionals
(vi) Encouraging private sector investment in the tourism industry
NECO HUMAN AND REGIONAL GEOGRAPHY
NUMBER THREE
(3a)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) Availability of Raw Materials: Pittsburgh is located close to rich deposits of coal and iron ore, which are essential raw materials for the steel industry. The proximity to these natural resources greatly reduced production costs and boosted industrial growth, especially in steel manufacturing.
(ii) Excellent Transportation Network: The city is well-connected by railroads, rivers (like the Ohio River), and highways, which makes it easy to transport raw materials to factories and finished products to markets. This accessibility played a key role in attracting industries to the region.
(iii) Skilled Labour Force: Pittsburgh has a large population of experienced and skilled industrial workers. Over time, generations of workers have been trained and employed in industrial activities, especially in steel production, making labour readily available and reliable.
(iv) Market Availability: The industrial region has access to large markets in cities like New York, Chicago, and other parts of the U.S. These markets provide steady demand for steel and manufactured goods, encouraging production and industrial expansion.
(v) Availability of Capital and Investment: There is an abundance of capital from banks and private investors in Pittsburgh and nearby financial centres. This access to finance supports the establishment and expansion of industries through the purchase of machinery, building of factories, and hiring of labour.
(vi) Government Support and Policy: The government of the United States has provided consistent support through favorable industrial policies, infrastructural development, tax incentives, and protectionist measures. This has encouraged the continuous growth of the Pittsburgh industrial region over the decades.
(3b)
=ADVANTAGES=
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) Economies of Scale: Concentration of industries leads to mass production, reducing production costs.
(ii) Easy Access to Skilled Labour: Workers with specialized skills are easily attracted to regions with many similar industries.
(iii) Efficient Use of Infrastructure: Industries share transportation, power, water, and other facilities, reducing overhead costs.
(iv) Growth of Supporting Services: Banks, insurance firms, and repair services thrive in localized industrial zones.
(v) Knowledge and Technology Sharing: Proximity allows companies to learn from one another and innovate more rapidly.
(vi) Boost to Regional Development: Localisation often transforms regions into economic hubs, boosting regional development.
=DISADVANTAGES=
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) Environmental Pollution: Concentration of industries often leads to air, water, and land pollution.
(ii) Overcrowding: Population and traffic congestion can occur in localized areas, causing urban problems.
(iii) Resource Depletion: Continuous industrial use may exhaust local natural resources.
(iv) Risk of Regional Decline: If demand falls or raw materials run out, the region may suffer economically.
(v) Labour Exploitation: High competition may lead to poor working conditions and low wages.
(vi) High Cost of Living: Localisation may push up the cost of housing and essential services in industrial areas.
NECO HUMAN AND REGIONAL GEOGRAPHY
NUMBER FOUR
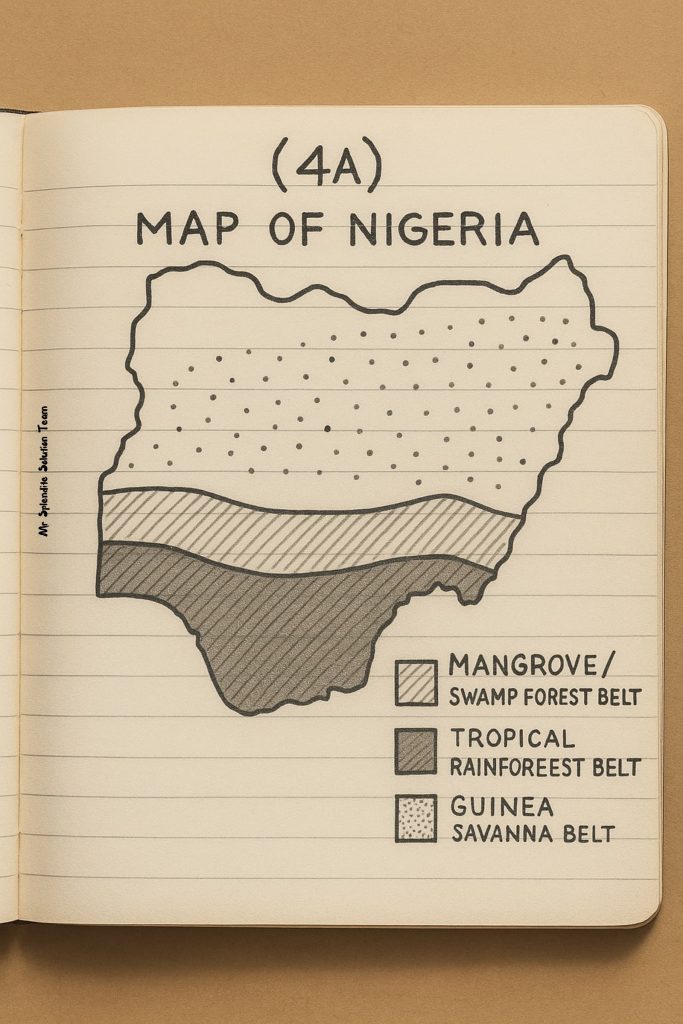
(4a)
Draw the diagram below
(4b)
(PICK ANY THREE)
(i) Broad leaves: Trees have large surface area leaves to absorb maximum sunlight for photosynthesis.
(ii) Drip tips: Leaves are shaped with pointed tips to allow rainwater to run off easily and prevent fungal growth.
(iii) Tall tree canopies: Forest trees grow very tall to reach sunlight in thick forests.
(iv) Buttress roots: Tall trees develop wide roots for support in the soft, wet soil.
(v) Evergreen leaves: Trees remain green year-round due to constant rainfall, aiding continuous growth.
(vi) Layered structure: Forests grow in layers (emergent, canopy, understory, forest floor) to efficiently use space and light.
(4c)
(PICK ANY THREE)
(i) Deforestation: One of the most serious threats to forest vegetation is deforestation, which is the large-scale cutting down of trees. This is often done for timber, agriculture, urban development, and fuel. When forests are cleared and not replaced, the natural habitat is destroyed, and the ability of the forest to regenerate is lost, leading to long-term environmental degradation.
(ii) Bush Burning: In many parts of Nigeria, especially rural areas, bush burning is a common practice used for hunting or clearing land for farming. These fires can easily spread beyond control, destroying large areas of forest, killing young trees, and leaving the soil exposed to erosion and nutrient loss.
(iii) Urbanization and Industrialization: As cities expand and industries develop, forests are often cleared to make room for roads, houses, factories, and other infrastructure. This rapid development reduces the size of natural forests and interrupts the balance of ecosystems, making it difficult for vegetation to thrive.
(iv) Overgrazing by Livestock: In savanna areas, excessive grazing by cattle, goats, and sheep can damage young trees and seedlings. Continuous overgrazing prevents new plants from growing and compacts the soil, which further hinders forest regeneration and reduces vegetation cover.
(v) Unsustainable Farming Practices: Farming techniques like slash-and-burn, shifting cultivation, and over-cultivation deplete the soil of nutrients and destroy vegetation. These practices make it hard for forests to recover after being cleared, especially when farmers do not allow the land to fallow or regenerate naturally.
(vi) Climate Change: Changes in temperature and rainfall patterns, caused by global warming, directly affect forest growth. Irregular rainfall can cause droughts that weaken trees and reduce plant diversity. Rising temperatures can also lead to the migration of plant species and the disappearance of those that cannot adapt.
NECO HUMAN AND REGIONAL GEOGRAPHY
NUMBER FIVE
(5ai)
=North West=
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) Kano
(ii) Kaduna
(iii) Sokoto
(iv) Katsina
(v) Zaria
(5aii)
=South East=
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) Onitsha
(ii) Aba
(iii) Enugu
(iv) Awka
(v) Nnewi
(5aiii)
=South West=
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) Lagos
(ii) Ibadan
(iii) Abeokuta
(iv) Akure
(v) Oshogbo
(5aiv)
=South South=
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) Port Harcourt
(ii) Warri
(iii) Calabar
(iv) Uyo
(v) Benin City
(5b)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) They facilitate the buying and selling of goods and services.
(ii) They provide employment opportunities for millions of Nigerians.
(iii) They generate revenue for the government through taxes and levies.
(iv) They promote industrial and manufacturing activities.
(v) They attract both local and foreign investments.
(vi) They serve as hubs for transportation and distribution of goods.
(vii) They encourage the development of infrastructure such as roads, markets, and banks.
(viii) They promote regional and international trade and economic integration.
(5c)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
Strategic location (e.g., near rivers, borders, or coastlines)
(ii) Availability of transport networks (roads, rail, seaports, airports)
(iii) Presence of natural resources and raw materials
(iv) Large population and market size
(v) Political and administrative importance
(vi) Industrial and economic activities
(vii) Availability of capital and financial institutions
(viii) Government policies and support for trade and commerce
(5d)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) Traffic congestion and poor road conditions
(ii) High cost of living and housing shortages
(iii) Environmental pollution (air, water, noise, and waste)
(iv) Insecurity and rise in crime rates
(v) Poor urban planning and overcrowding
(vi) Inadequate public services such as electricity, water, and waste management
NECO HUMAN AND REGIONAL GEOGRAPHY
NUMBER SIX
(6a)
A cottage industry is a small-scale, home-based manufacturing activity typically operated by individuals or families using local raw materials and simple tools. These industries usually require low capital, involve manual labor, and produce goods for local or limited markets.
(6bi)
(i) Traditional Cottage Industries: These are the oldest form of cottage industries that rely on indigenous skills passed down through generations. They involve the use of simple tools and local raw materials. Examples include pottery, weaving, blacksmithing, and mat-making. These industries are usually informal and aimed at serving the local community.
(ii) Modern Cottage Industries: These are more organized and sometimes semi-mechanized home-based industries. They may involve small machines and better production techniques compared to traditional ones. They often produce goods for wider markets and may receive support from government or cooperative societies. Examples include tailoring shops, local food processing, and craft making.
(6bii)
(PICK ANY FOUR)
(i) They are operated on a small scale.
(ii) They are usually home-based or located in small workshops.
(iii) They make use of local raw materials.
(iv) They require little capital to start and run.
(v) Labor is mostly provided by family members or locals.
(vi) They use simple or traditional tools and equipment.
(vii) They have low output and limited production capacity.
(viii) Their products are often handmade or semi-finished.
(6c)
(PICK ANY TWO)
(i) Availability of Raw Materials: Many rural areas have abundant natural resources such as agricultural products, clay, wood, and minerals, which serve as raw materials for cottage and small-scale industries.
(ii) Cheap Labor: Labor in rural areas is relatively cheap due to the high level of unemployment and low cost of living. This reduces the overall cost of production.
(iii) Proximity to Source of Raw Materials: Locating industries near the raw material source helps reduce transportation costs and minimizes delays in the supply of inputs.
(iv) Low Cost of Land and Operation: Land and other operational costs like rent, water, and electricity are generally cheaper in rural areas compared to urban centers, making it more economical to operate.
ANSWERS completed…..

Follow us then so you will have it on time
sir what about tomorrow geography essay
Yes sir. We will update it
Sir what about goegraphy essay tomorrow